
“How do I start learning SEO?”
It’s the question I hear most often, and for good reason. There’s so much to learn about SEO that many beginners get overwhelmed.
I’ve trained dozens of SEO professionals and found that hands-on experience trumps theory every time. With SEO tools, you can see exactly how successful websites rank—their content strategies, keyword targets, and technical setups are all there to study and learn from.
But like any profession or skill, it’s important to conquer the fundamentals and then move on to more advanced topics.
Remember, expanding your SEO knowledge is a marathon, not a sprint—it takes time. However, if you keep at it, you’ll gain the experience and skills necessary to launch a successful career as an SEO expert.
In this guide, I’ll share my proven process for learning SEO. You’ll discover how to build your skills step by step, from core concepts to advanced strategies, while gaining invaluable practical experience.
3 Best Ways to Learn SEO
There are many ways to learn SEO.
Some people master the fundamentals with free resources, like YouTube or blogs. Others prefer learning from experts in SEO courses to save time and speed up the learning process.
Ultimately, it’s up to you to decide what methods work best for you.
SEO is always changing, so you’ll need to keep learning and trying new things to stay up-to-date. Keep these three effective methods in mind as you start your journey.
1. Learn by Doing
The most effective way to learn SEO is to put your knowledge into practice.
Launch a blog to learn all the ins and outs of website growth. Today, it’s easier than ever with platforms such as WordPress, Wix, or Squarespace.

A personal website is not just a learning tool. Over time, a well-performing site can help you land SEO clients, position you ahead of other candidates, and could even turn into a profitable side hustle—or replace your full-time job.
Once your blog is up and running, start with the basics (don’t worry, I cover these in more detail below):
- Experiment with keyword research: Try to rank your website for multiple keywords to better understand keyword research and Google’s content quality standards
- Apply on-page and off-page SEO strategies: Use what you learn about site structure, content quality, and backlinks to improve user experience and increase web traffic
- Refine your SEO copywriting: Launching a blog is also an excellent way to nail essential SEO copywriting skills. Craft content that engages readers and ranks well.
2. Read SEO Blogs
If you’re into reading, I recommend learning SEO through various tutorials and blogs. The web is full of SEO resources, so you’ll find exactly what you’re looking for.
By regularly reading reputable SEO blogs, you can gain a solid understanding of the fundamental concepts of SEO, including backlink analysis and technical SEO, to name a few.
Additionally, SEO blogs provide insights into the latest trends and algorithm updates, keeping you ahead of the competition. As SEO algorithms evolve, blogs often feature articles that analyze these changes and offer strategies to adapt your SEO approach accordingly.
Later in this article, I’ll share some SEO blogs you’ll want to bookmark. (If you’re, ready, click on this link to check the list).
3. Take SEO Courses
There are many free and paid SEO courses available for all experience levels that can seriously boost your knowledge and credentials.
Here’s where to start:
- Semrush Academy: Offers free SEO and content marketing courses, including those by SEO heavyweights like Brian Dean and Nathan Gotch. You can also earn a certificate from Semrush’s courses, which would make an excellent addition to your CV.
- Yoast SEO Academy: Get a crash course on SEO from the makers of the popular SEO plugin, Yoast SEO. The Yoast SEO Academy includes free and paid, beginner-friendly training on SEO, WordPress, structured data, and more.
- Traffic Think Tank Academy: A paid subscription provides access to expert-taught tutorials and courses on link building, technical SEO, and much more. You’ll get content for every skill level, from beginner to advanced, so you’ll never run out of things to learn and level up on.
With these resources, you’ll be equipped to kickstart a successful SEO career.
How to Get Started with SEO: Key Concepts and Tools
Getting started with SEO is easy if you have a solid foundation of knowledge.
If you’re new to SEO, I recommend reviewing the SEO fields mentioned below.
SEO Fundamentals
Start with basic SEO concepts first. It will help you understand how search engines work and how to get your content on Google.
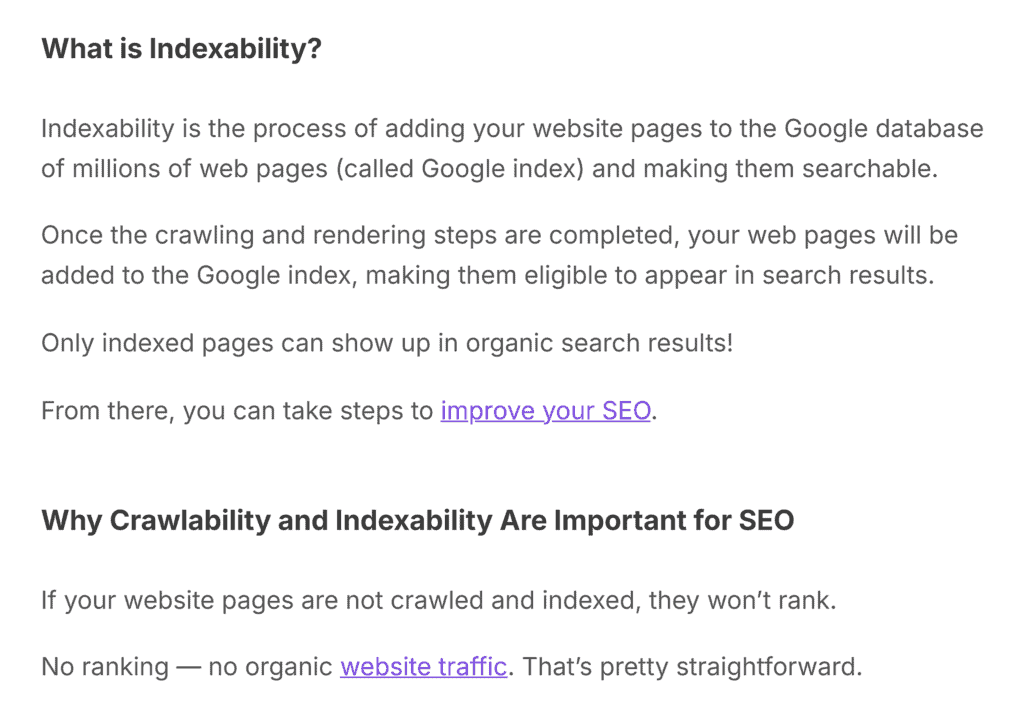
As an SEO specialist, you must ensure a Google bot can crawl and index your website without any 4xx errors. If your content isn’t indexed, it won’t rank.

You’ll also need to understand how Google algorithms work.
It’s a lot, I know. However, every SEO specialist has to understand these concepts to run SEO audits and make data-driven decisions.
I recommend starting with Google’s Search Engine Optimization (SEO) Starter Guide. It’s a go-to source for beginners and SEO experts to learn about up-to-date Google strategies.
Keyword Research
If you don’t optimize your content for any keywords, it’s unlikely to rank well (or at all).
Regardless of what people say on the web, Google still pays attention to keywords in the metadata and on webpages to better understand your page.
Here’s what John Mueller, Senior Webmaster Trends Analyst and Search Relations team lead at Google, says:

If your goal is to grow your website’s organic traffic, keyword research should be an essential part of your SEO strategy and the first step of your content creation process.
To start, you’ll need to know these terms:
- Search intent: The purpose behind a user’s search—whether they want to learn something (informational), buy something (transactional), find a specific website (navigational), or research products before buying (commercial)
- Search volume: The number of times a keyword is searched monthly. Higher isn’t always better since specific terms often convert better.
- Keyword difficulty: How hard it is to rank on Google’s first page for a term, usually scored 0-100. Higher scores mean tougher competition.
Tools like Semrush, Answer the Public, Google Trends, Google Search Console, and Ubersuggest can help you with keyword research.

If your website is new or has a low domain authority, I recommend targeting long-tail keywords, as they have less competition and a higher conversion rate.
TTT has an excellent course on “How to find untapped keyword opportunities,” where Nik Ranger, a technical SEO expert, teaches you how to conduct keyword research.

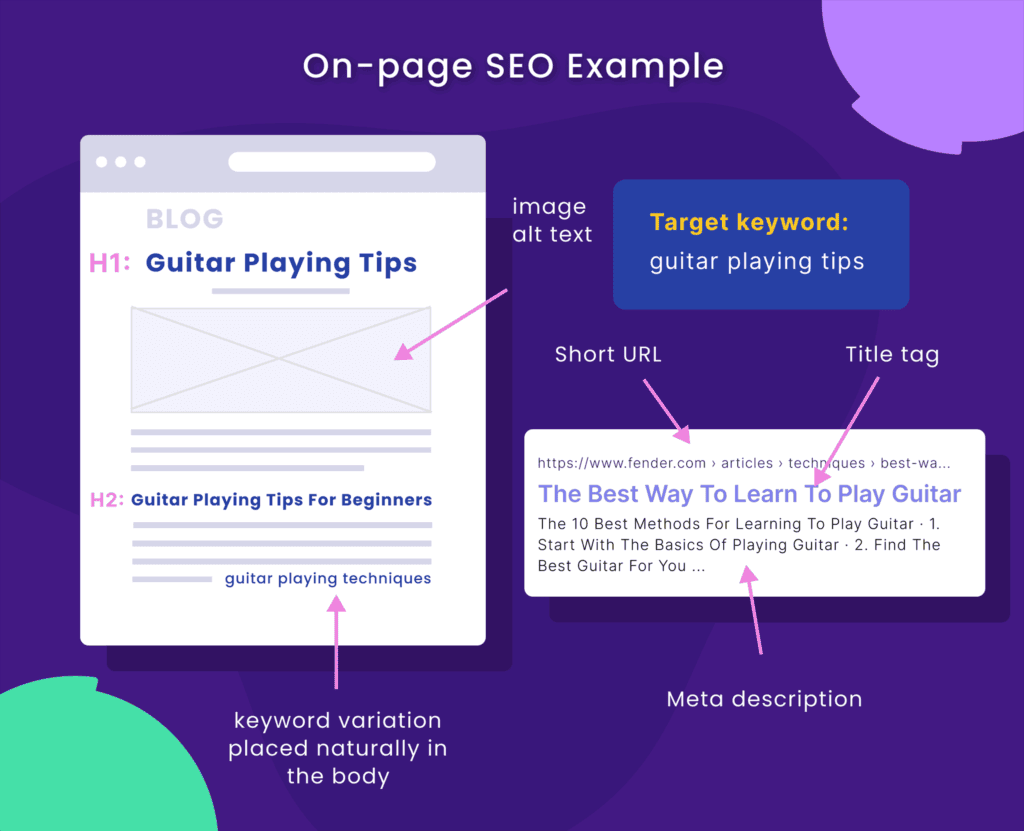
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO is about optimizing your webpage’s content to improve rankings.
In a nutshell, on-page SEO includes:
- Content: Creating content that aligns with user search intent and target keywords
- Title tags: Crafting compelling title tags that accurately reflect your content and include relevant keywords
- Meta descriptions: Writing concise and informative meta descriptions that accurately summarize your page’s content and encourage users to click
- URLs: Creating short and clear URLs with relevant keywords
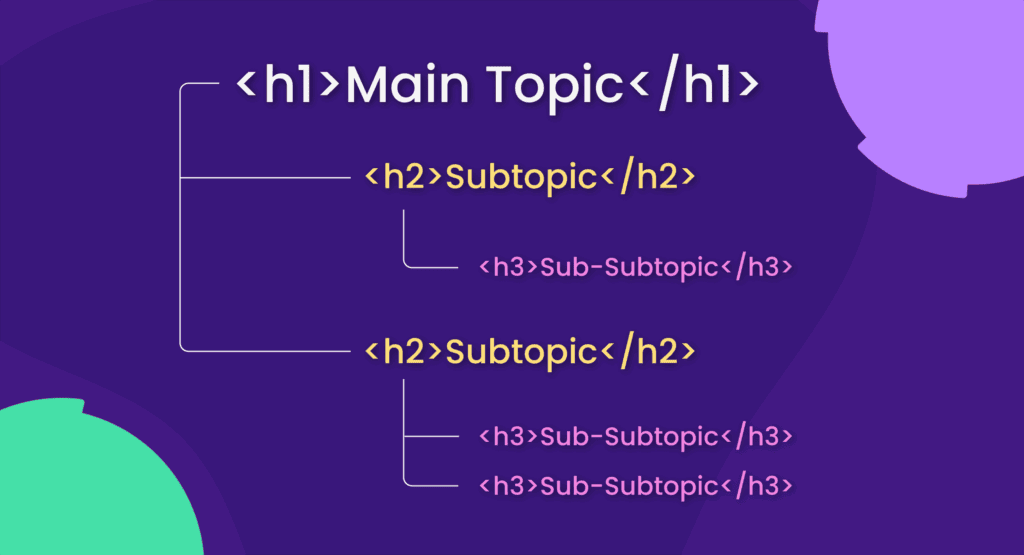
- Headers (H1, H2, H3, H4): Using header tags appropriately to organize and highlight critical information on your page
- Internal linking: Strategically linking to other relevant pages on your website to improve navigation and page authority
- Image optimization: Optimizing image file names, alt tags, and sizes to reduce page loading speed and improve image search rankings
These elements help Google better understand your content and rank it for your target keywords.
Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO includes activities done off your website. Common strategies include link-building, PR, and influencer marketing, to name a few.

Off-page SEO is important because backlinks are still among the top Google ranking factors. Simply put, the more high-quality backlinks your website has, the more authoritative it is in Google’s eyes.
So, if you focus on off-page SEO, your main tasks will be running backlink audits, link building, outreach, and guest posting.
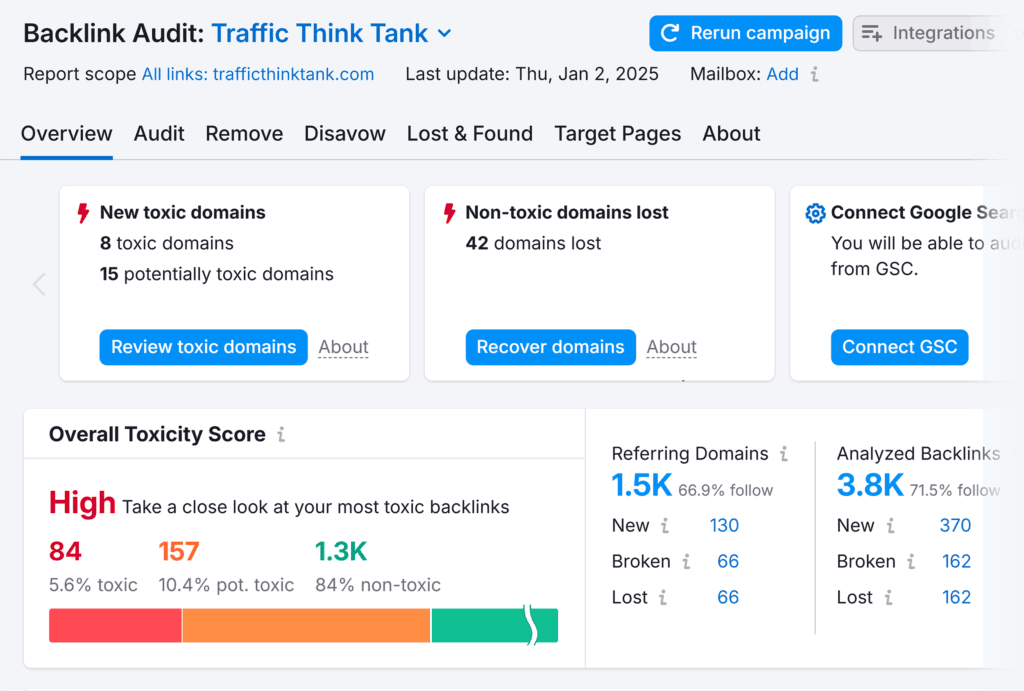
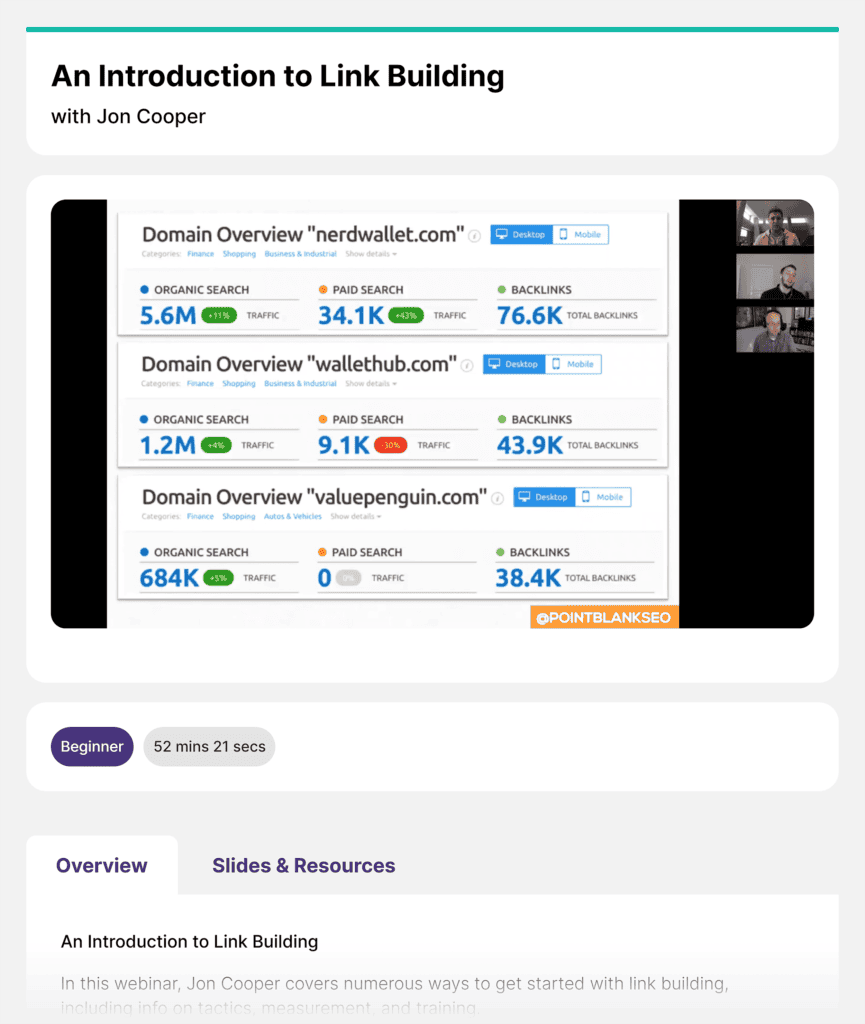
You’ll need different tools depending on your strategy. In the image above, for example, you can see I used Semrush’s Backlink Audit tool.
Other tools like Ahrefs and Moz Link Builder would also work well.
Based on my experience, off-page SEO is much more challenging to control than on-page SEO. That’s because Google is against sponsored backlinks, and building high-quality backlinks requires persistence and patience.
Some website owners often get impatient and use black hat SEO strategies, such as PBN backlink networks. However, the recovery period will be long and painful if your website gets a Google penalty.
Even if you build links from reputable websites, it’s not guaranteed that your website’s domain authority (DA) will grow and rankings will improve. Nevertheless, every full-stack SEO should know how to build backlinks.
TTT Academy has over 20 lessons on link building with proven-to-work strategies from SEO experts.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO helps search engine bots discover, crawl, and index your website pages.
The primary goal of technical SEO is to ensure the crucial pages on your website are indexed while other pages are excluded from the Google index.
If you want to start with tech SEO, here are a few common tasks you’ll perform:
- Page speed optimization
- Creating sitemaps
- Fixing issues associated with Core Web Vitals
- Making your website mobile-friendly
- Updating broken pages
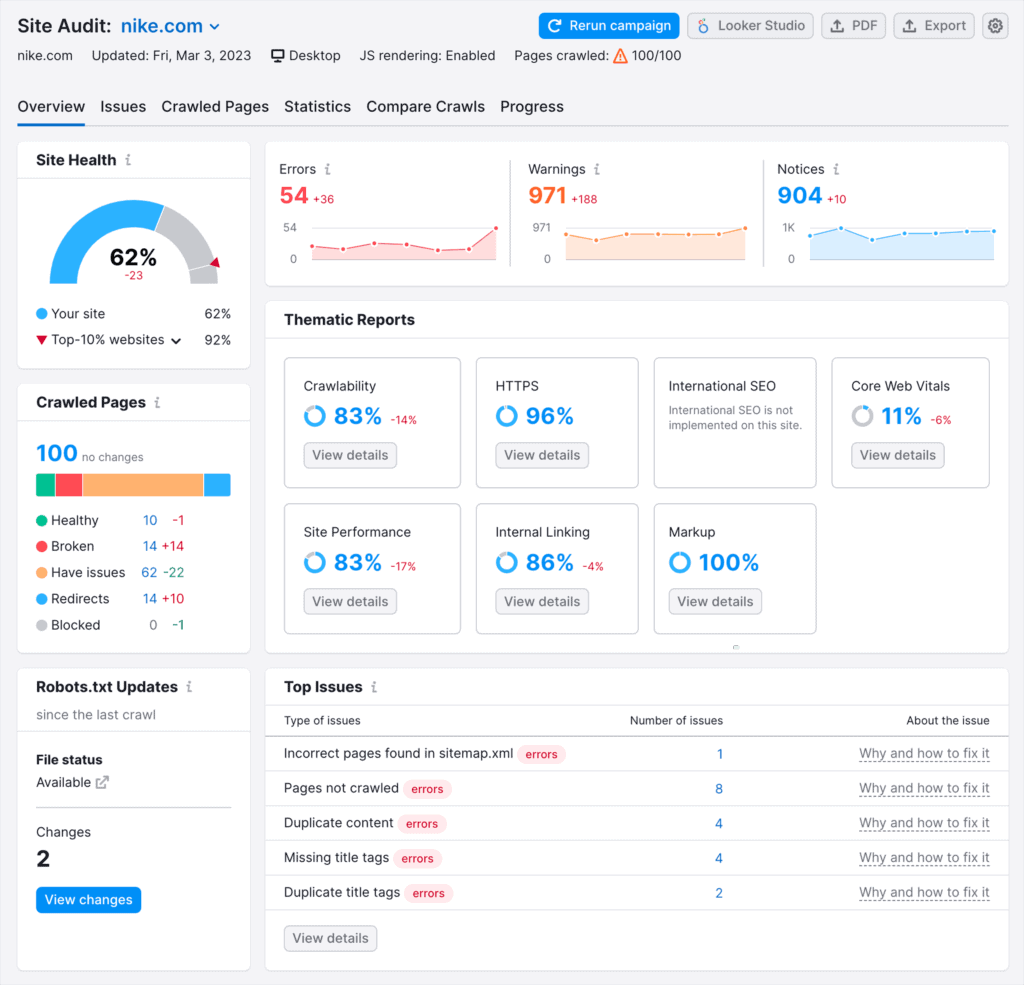
Luckily, Semrush and other SEO tools can help you conduct site audits and discover many technical issues on your website. But you’ll still have to understand what causes them, how to prioritize issues with the highest impact, and how to fix them.
SEO Tools
SEO is easy when you know which tools to use.
I recommend starting with Google Search Console, Google Analytics (GA), and Google Tag Manager (GTM). These are free tools for website performance tracking and analysis.
Google Tag Manager is a free tag management system that lets you easily add, edit, and remove tracking tags from your website without touching a line code.
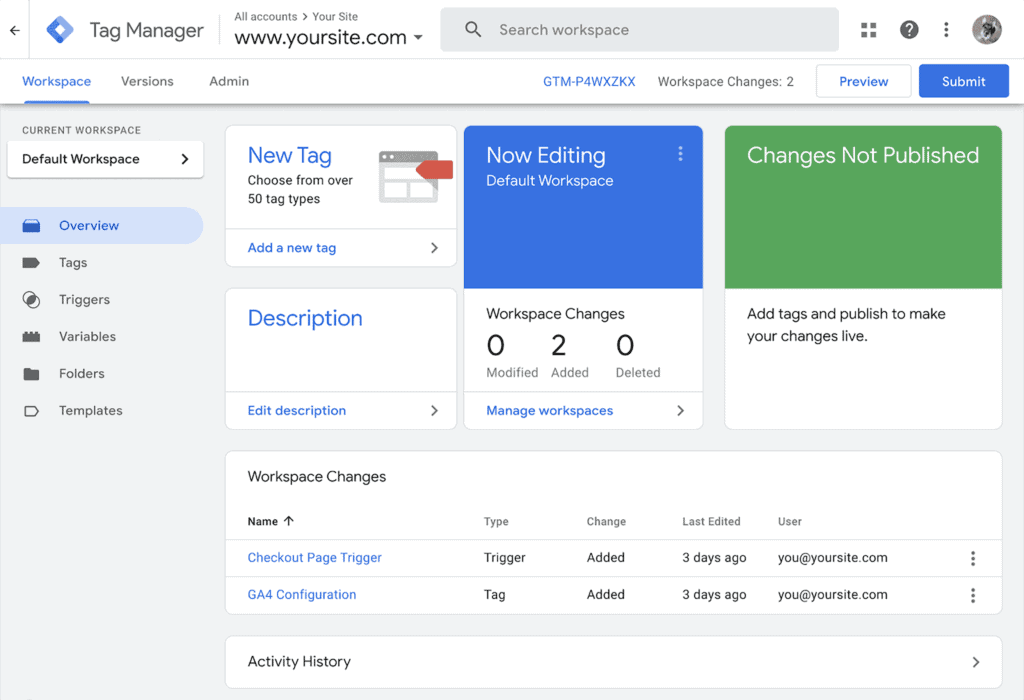
You can use GTM to add tracking tags to your website, including GA, Meta Pixel (former Facebook Pixel), Hotjar, or Google AdSense tracking code.
Google Analytics is the most accurate tool for tracking traffic to your website and user behavior. It helps you understand how visitors interact with your content and where they come from.
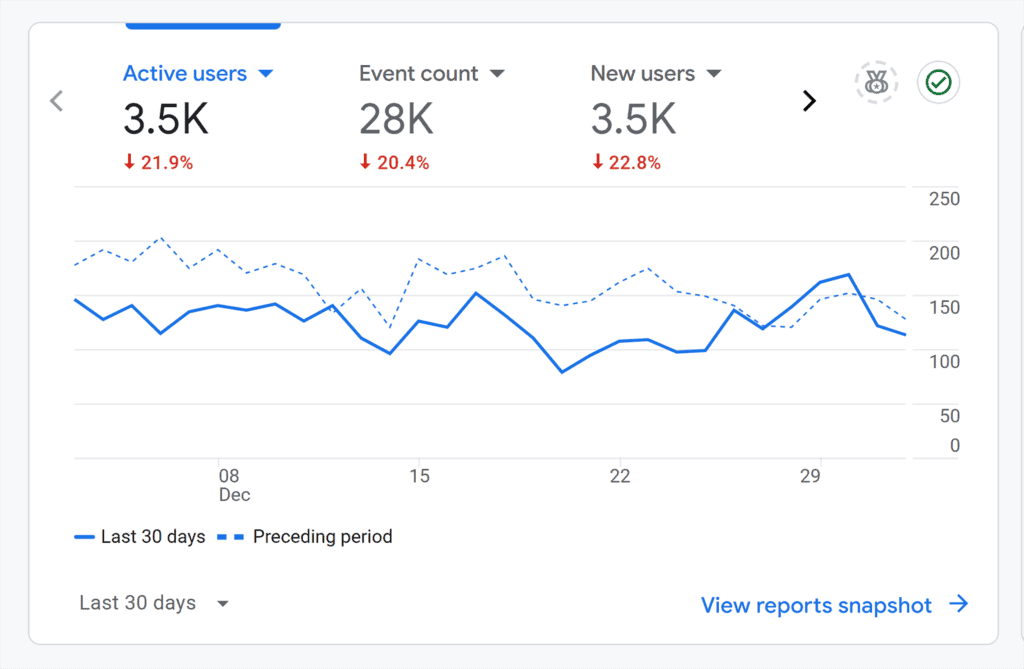
Google Search Console will help you track your website’s performance in organic search results and whether any technical errors occur.
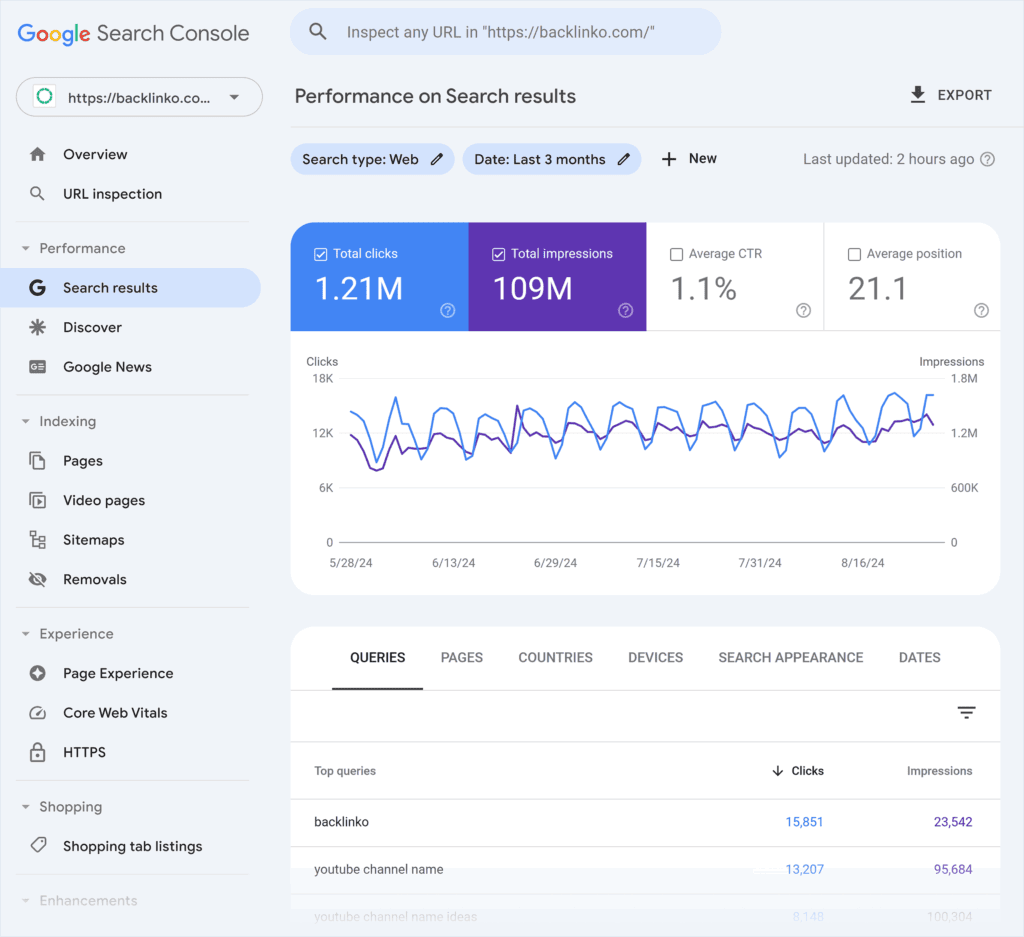
Google’s tools are suitable if you only work on your website. However, if you want to spy on your competitors and analyze their strategies, use professional SEO tools like Semrush for deeper insights.
Semrush is an all-in-one, powerful digital marketing toolkit with more than 55 different tools and reports.
With Semrush, you can analyze website domains, check competitors’ top-performing pages, see their top-performing keywords, and explore their traffic acquisition sources. You can learn more about the tool in our Semrush review.
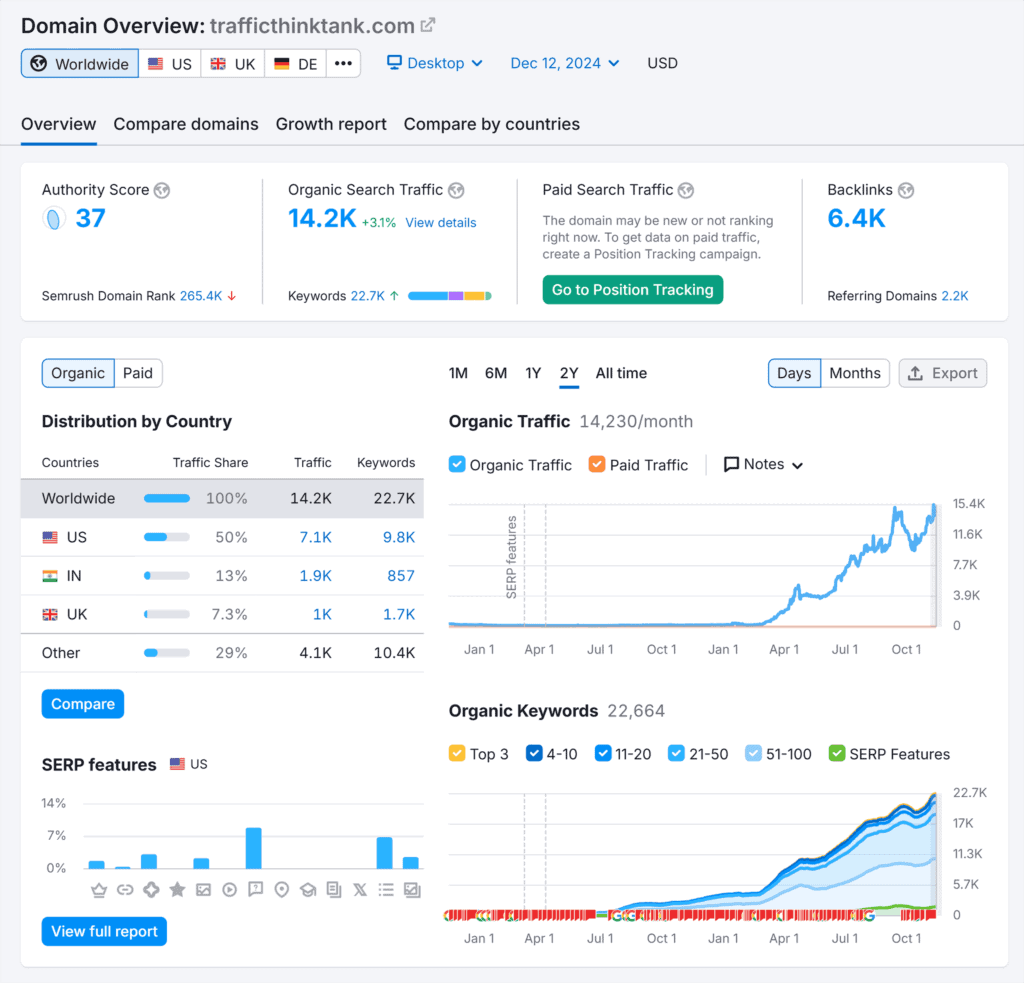
SEO for Content Management Systems (CMS)
WordPress is the most popular content management system (CMS), which lets you launch a website and publish content without coding skills.
But even CMS-powered websites need to be optimized to rank well on Google. Fortunately, WordPress has SEO plugins that make this process easier.
A plugin is a small software add-on you can install on your WordPress website to add new features or improve existing ones.
These plugins are designed to help you improve your site’s SEO without needing technical expertise. For example, I use All In One SEO on my WordPress site, which gives me an SEO score (currently 87/100) and flags technical issues I need to address.
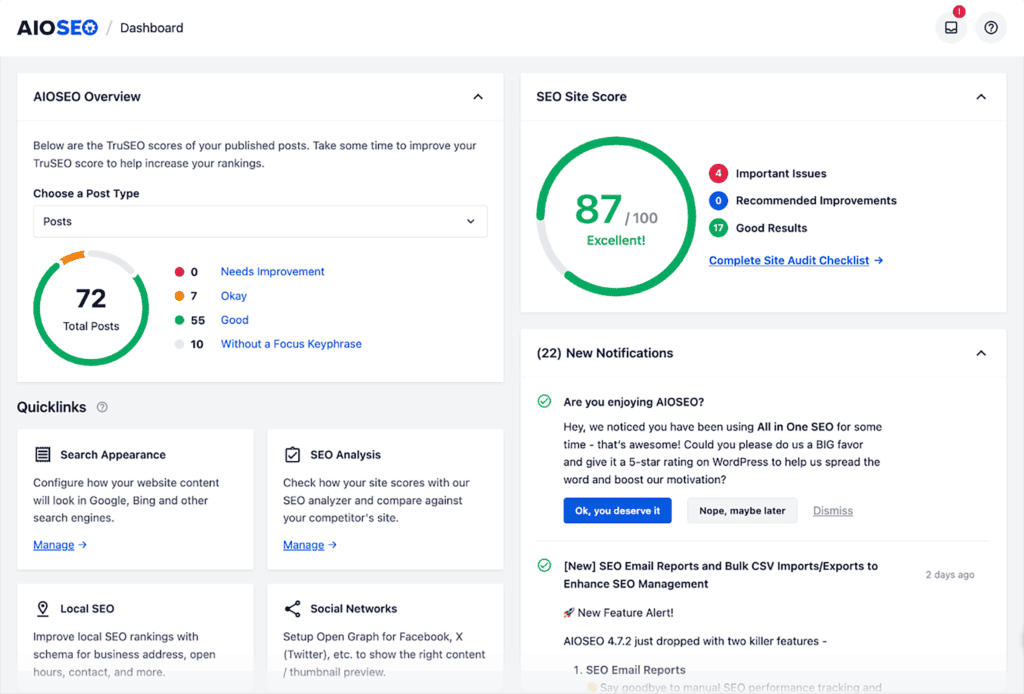
These plugins let you add meta descriptions and title tags, generate a sitemap, set up 301 redirects, and more.
Since CMS platforms are generally intuitive, you can implement these technical SEO improvements without a developer.
For a detailed walkthrough on optimizing CMS websites, check out this WordPress SEO Guide. It covers everything you need to know to boost your site’s visibility on search engines.
How to Practice SEO on Your Own Site
Reading about SEO can only get you so far. Now, it’s time to put what you learned into action.
Below, I’ll show you step-by-step how you can get started with SEO by launching your own website.
Buy a Domain and Hosting
If you want to practice SEO, there’s no better way than on your own site.
Whether it’s a niche, informative site, or a site to promote your SEO services, you’ll need to select a domain name that’s catchy and concise.
Next, choose a hosting provider. Picking the right setup at this stage can make a big difference in your site’s speed and uptime.
Here are a few popular options:
- Bluehost: A basic choice for WordPress sites, known for its ease of use. Plans start at $2.95 per month, making it budget-friendly if you’re just getting started.
- SiteGround: Ideal if you’re looking for strong customer support and reliable uptime. SiteGround integrates well with WordPress and offers free daily backups. Plans start at $2.99 per month.
- Namecheap: For those who prefer flexibility, Namecheap’s domain registration services are affordable, and their hosting packages are scalable, with basic plans starting at around $1.98 per month.
- HostGator: Known for its easy-to-navigate platform and unlimited storage, HostGator’s shared hosting plans start at $2.75 per month and can be a good choice if you expect your site to grow.
Take time to weigh what matters most to you—budget, support, or features—to set your site up for long-term growth.
Set Up a WordPress Website
Why WordPress when there are so many other CMSs out there?
For one, it’s the world’s most popular content management system, powering 43.7% of all websites globally.
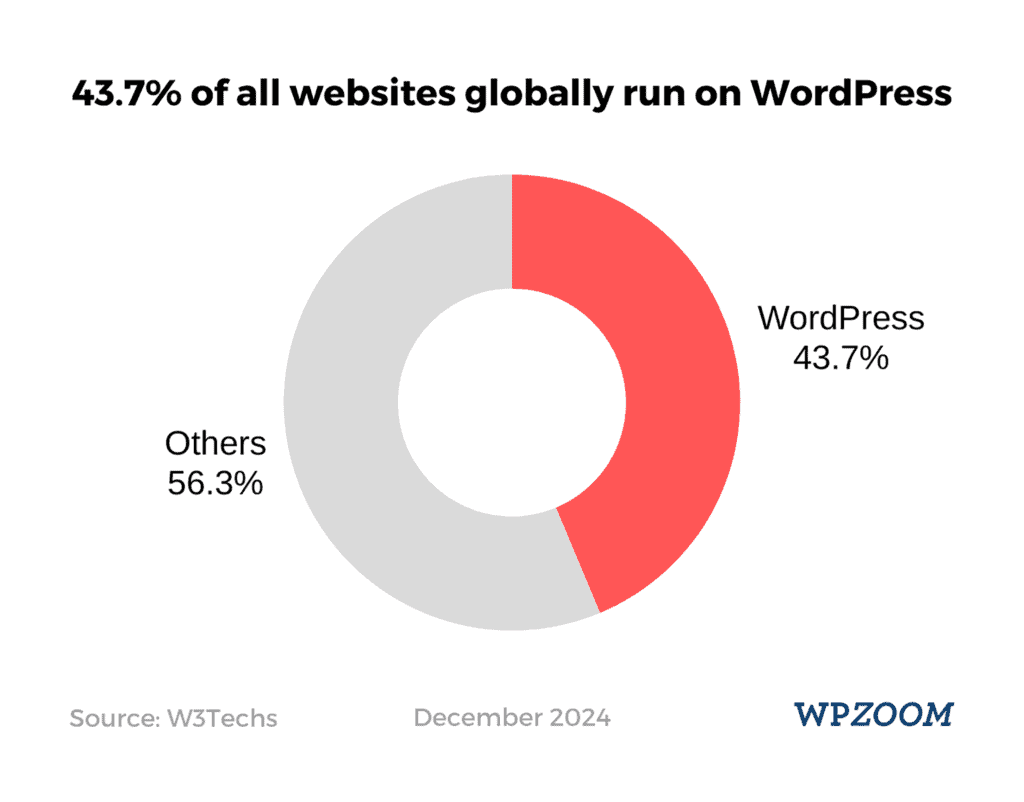
But WordPress’s plugins, themes, and templates also make it an ideal platform for practicing SEO, offering tools for optimization, speed, and mobile responsiveness that can enhance your site’s ranking.
Experimenting with these tools lets you apply and refine SEO techniques, helping you grow your site’s visibility.
Now, it’s worth noting that you’ll stumble upon two WordPress websites in search results:
- WordPress.com (hosted): A platform that supplies everything you need to build a website using WordPress software
- WordPress.org (self-hosted): The software itself, which you can use to build and maintain a website on your own
I highly recommend going with the self-hosted WordPress option, as it gives you full control over SEO and monetization.
Take care of the setup yourself, or bring in a developer to do it for you.
When it comes to your website’s user interface (the design), you’ve got three options:
- Create a custom design from scratch (this takes time and resources)
- Use drag-and-drop builders like Elementor
- Pick and install a pre-made design theme
The second and third options are beginner-friendly and should be more than enough to give you a feel for launching a website.
In fact, I still run one of my websites using Elementor because it’s so simple to create and edit static pages like the homepage and About page.
Install SEO Plugins
WordPress has a big library of plugins for various needs. Although many of these plugins are entirely free, there are also premium options that include basic SEO features at no cost, like Yoast SEO and All In One SEO.
With Yoast SEO, you can tweak things like meta titles, descriptions, URL slugs, and structured data while seeing how they look in real time. It also simplifies sitemap creation and helps search engines better understand and navigate your website.
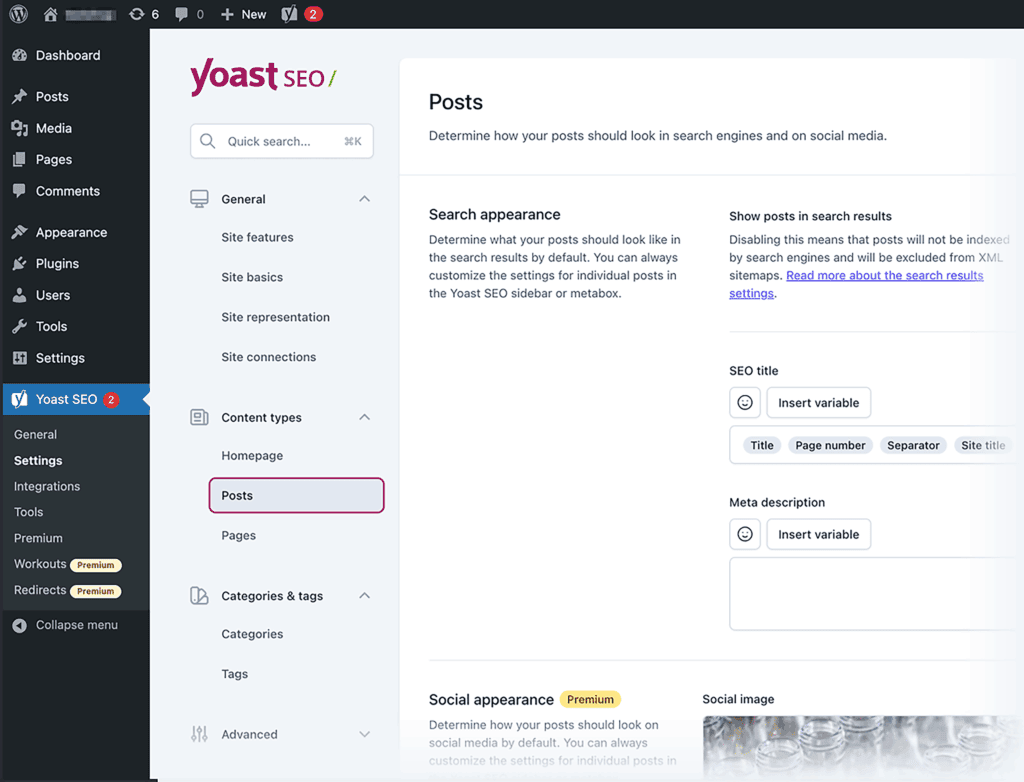
I’ve been using the All In One SEO (AIOSEO) plugin for several years to manage my website. So, I can speak about this one from my experience.
It lets me customize metadata and sitemap settings, create schema markup, and get on-page recommendations for every page.

The free version is pretty solid, but the paid one gives you way more options for tracking your site’s technical performance and fixing any potential issues.
For example, AIOSEO Pro lets you create and manage redirects, so you won’t need a separate plugin for that.
In my experience, having too many plugins can cause conflicts and might even slow down your site’s loading speed. So, it’s best to only install the plugins you need.
Conduct Keyword Research
Now you know the basics of setting up a simple website using WordPress. The next challenge is figuring out how to create content that actually ranks.
What you write about depends on your goals, but I suggest starting with some quick keyword research to see the search queries in your niche.
Let’s say you want to write about hiking.
If you’re an experienced hiker, you probably have a good sense of what beginners want to know. I suggest using Semrush’s Keyword Magic Tool to discover related topics with solid search volume.
Here’s how it works.
Open Keyword Magic Tool, insert your seed keyword, and click “Search.”
Semrush will generate thousands of keyword ideas related to hiking that you can use to write content for your website.
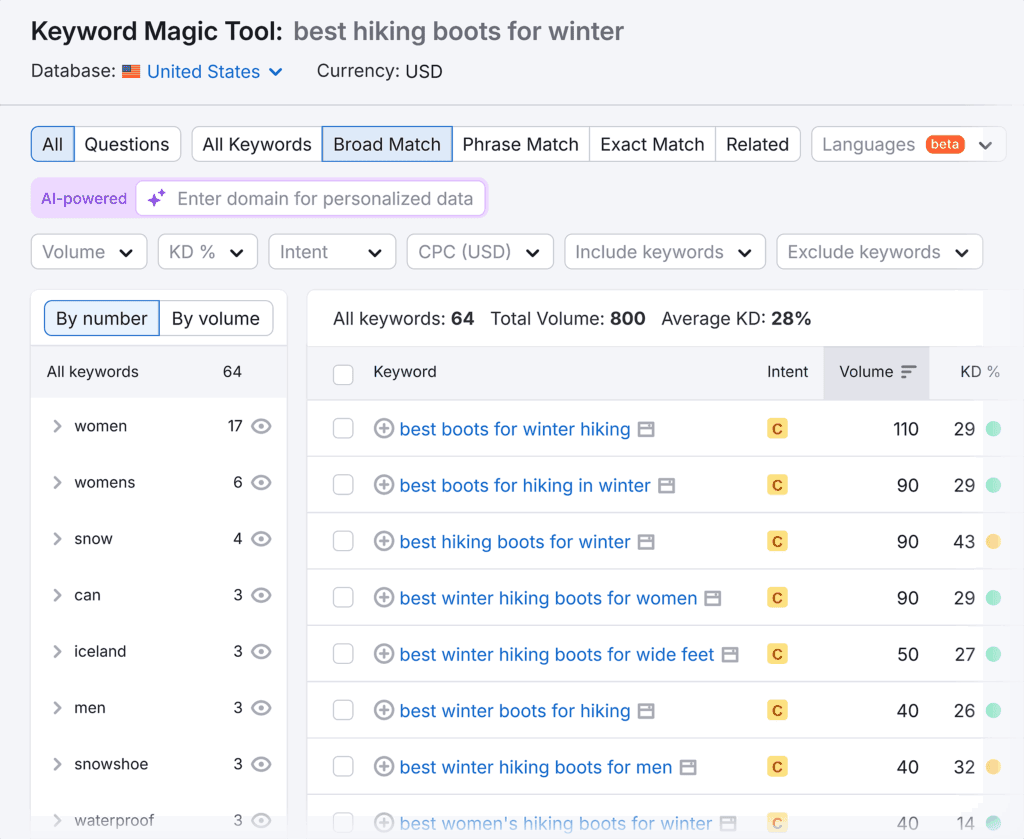
To narrow the list, filter keywords by search intent, keyword difficulty, and search volumes.
Since you’re launching a new website, focus on easy-to-rank keywords. Find them by clicking on “KD%” and selecting “Very easy” or “Easy.”
Semrush will now display hiking-related keywords that have the least competition.
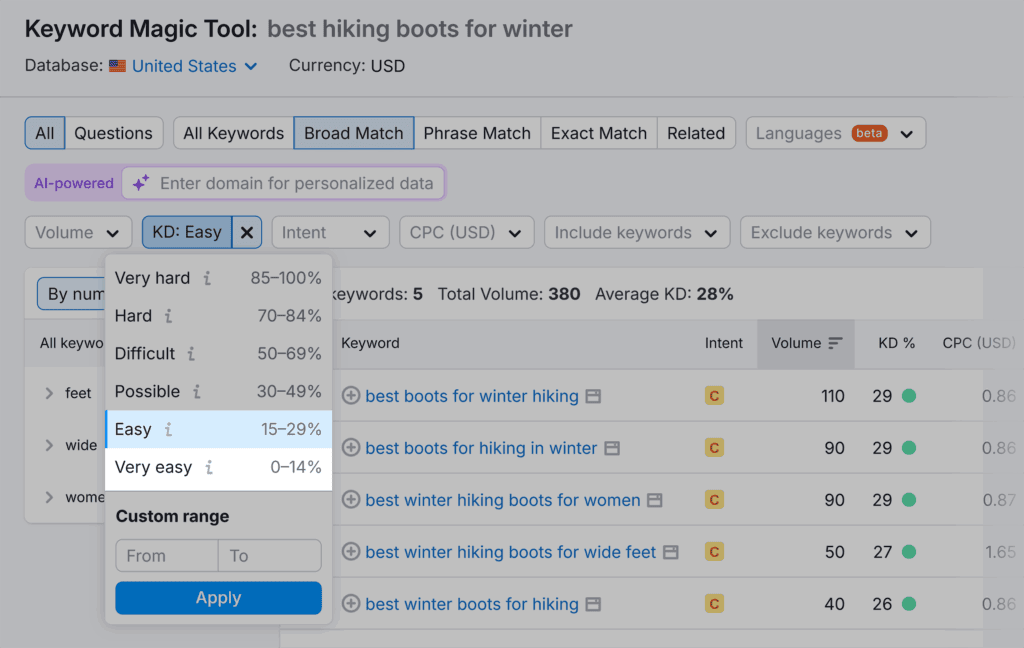
For instance, “best hiking boots for winter” would be a great topic to choose because it has low keyword difficulty and monetization potential.
Create SEO-Friendly Content
Once you know your target keyword, it’s time to create high-quality content.
Cover the topic thoroughly to address what users are looking for. If your content doesn’t align with their search intent, they’ll likely bounce from your page.
Key optimization elements:
- Add your target keyword naturally throughout each page
- Break text into short paragraphs (2-3 sentences)
- Include visuals with optimized alt text
- Add internal links to related content
- Include authoritative external references
- Structure content with descriptive subheadings
Optimize On-Page Elements
A key aspect of SEO content writing is incorporating keywords. While metadata doesn’t directly affect your rankings, it can improve your organic click-through rate (CTR).
You’ll want to make sure your keyword shows up in key spots like the:
H1
Keep your keyword close to the beginning of the H1 (headline), if possible. Ensure the headline is compelling enough to attract clicks.
Aim for a title length of 50 to 60 characters to ensure it displays well in search results.

First Paragraph
Introduce your keyword naturally within the first 100 words. This helps signal relevance to search engines and ensures the topic is clear to readers immediately.
Subheaders (H2s, H3s)
Use your keyword or variations in subheaders to structure the content and maintain relevance throughout.
Subheaders should guide the reader and include keywords without sounding forced.
URL Slug
Keep your URL short and descriptive, using only the main keyword or a slight variation. Avoid special characters and unnecessary words.

Image Alt Tag
Describe the image using the keyword if it fits naturally, and keep it brief but descriptive. Aim for 125 characters or fewer, as this helps with accessibility and image search.
Title Tag
Include your keyword at the beginning of the title tag when possible, keeping the full title around 50 to 60 characters. This tag is critical for click-through rates, so make it relevant and engaging.
Meta Description
Write a compelling summary including the keyword, aiming for under 155 characters.
Check out this insightful on-page SEO guide from Semrush to learn more.
Build Backlinks
Building a solid backlink profile is essential for increasing your domain authority and competing for high-ranking keywords.
When I started my WordPress website, I knew time was limited, so I focused on high-impact activities. I began by optimizing content and researching long-tail keywords to target less competitive terms.
As my rankings improved, I realized that strengthening my domain authority through backlinks would be the next critical step so I could target more competitive keywords.
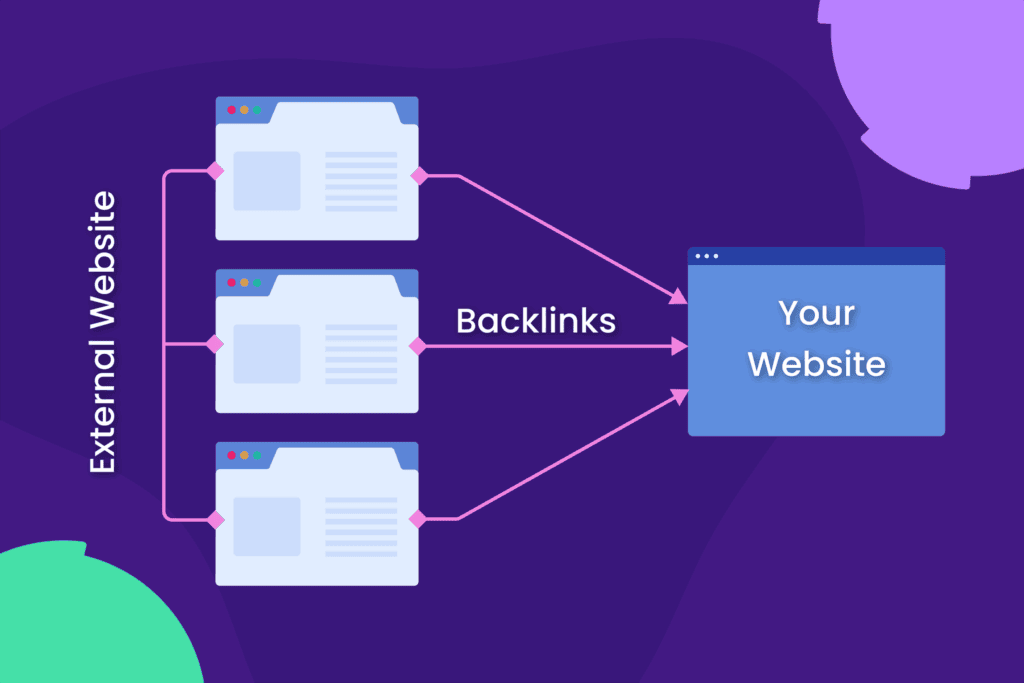
So, how can you build these links? Here’s a quick rundown of effective strategies:
Guest Blogging
Write articles for industry-relevant websites, positioning yourself as an expert while earning backlinks. Focus on quality over quantity—pitch to sites that align with your niche and have engaged audiences.
Resource Pages
Many websites create resource pages filled with helpful links. Reach out to site owners and suggest your content as a valuable addition to their list, especially if you have unique resources that fill a gap.
Broken Link Building
Find broken links on relevant websites and offer your content as a replacement. This not only helps the site owner but also brings you a quality backlink.
A backlink analytics tool that tells you lost backlinks can help you identify sites to contact.
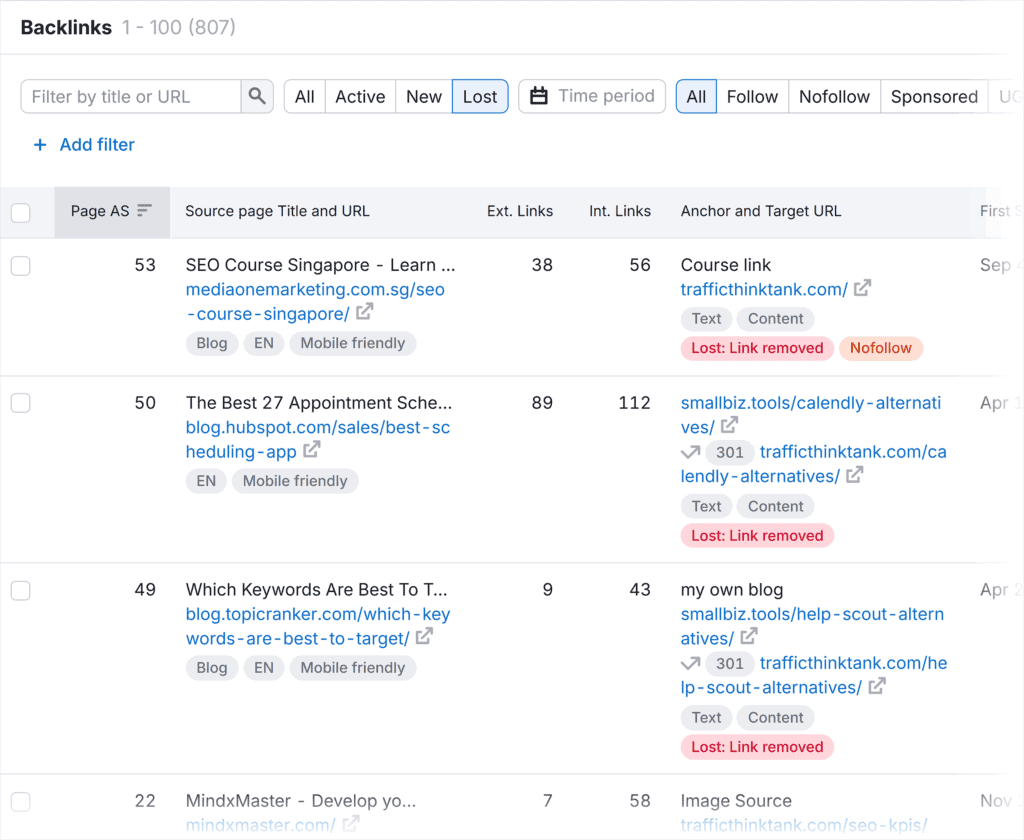
Network Online
Join forums, LinkedIn groups, or Reddit threads related to your industry. By sharing valuable insights and your content (where relevant and allowed), you can gain natural backlinks from engaged readers.
If you want to learn this tactic more in-depth, I recommend checking out Backlinko’s link-building guide. It’s filled with case studies, examples, and Brian Dean’s expert tips to help you land high-quality backlinks.
Use Analytic Tools
Adding the following tools to your workflow will let you practice SEO with real-time data, fine-tuning your strategy for better results:
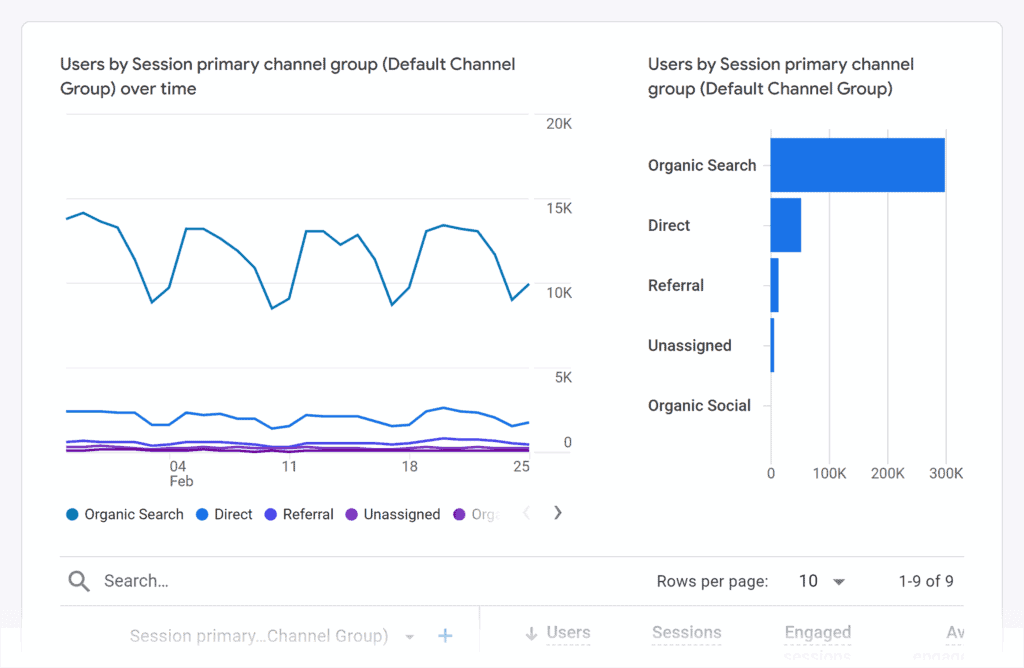
Google Analytics
GA is essential for tracking traffic, bounce rate, user behavior, and conversions.
Dive into the Behavior and Acquisition reports to uncover user paths, top-performing pages, and potential content improvements.
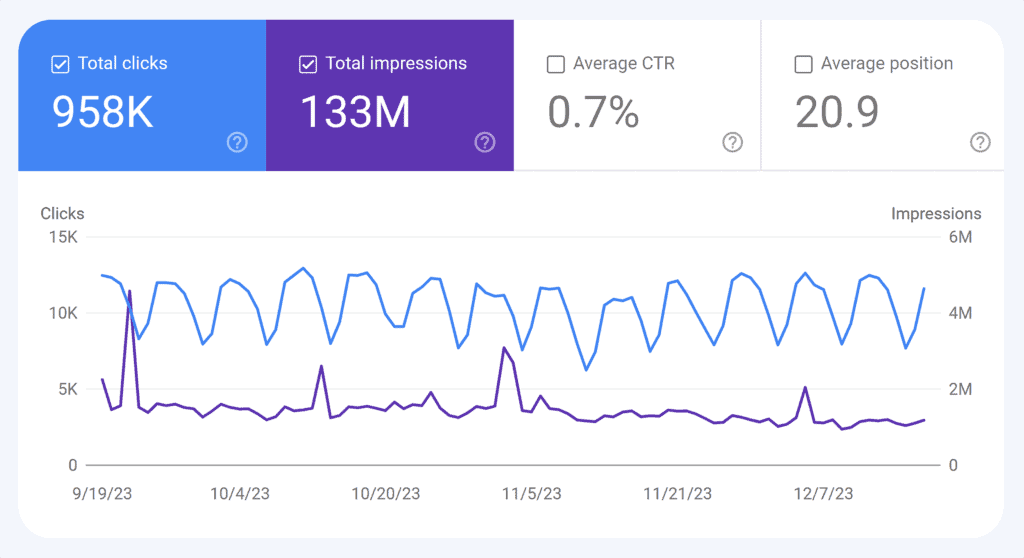
Google Search Console
Critical for monitoring your site’s health, indexing, and click-through performance.
It provides keyword insights, identifies technical issues, and offers opportunities to optimize for higher site rankings. Also, it’s free!
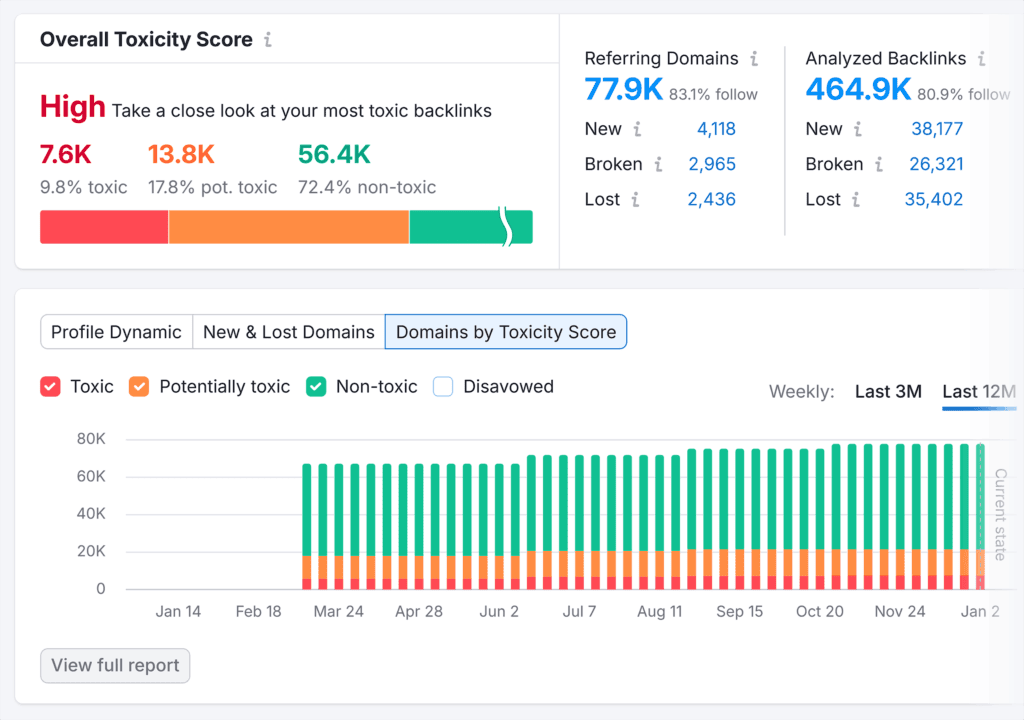
Semrush
Great for in-depth keyword tracking, site audits, and backlink analysis. Use it to benchmark your performance, find SEO opportunities, and manage your backlink profile.
Monitor Your Performance
To gauge your website’s performance, set clear business goals and align SEO metrics with them.
Regularly track your SEO key performance indicators (KPIs) to identify trends, spot issues, and measure progress against your goals.
Schedule periodic reviews to adjust strategies based on data insights.
Here are essential SEO KPIs to monitor, plus tips on how they can help you refine your strategy:
Organic Impressions
Track how often your site appears in Google search results with Google Search Console.
High impressions with low clicks may indicate a need to optimize your titles or meta descriptions. Consider what makes you click on a search listing and apply these findings to your metadata.

Organic Traffic
Measure the total number of visits from search engines. Use Google Analytics to segment organic traffic by page, device, and location, helping you see which content resonates most with different audiences.
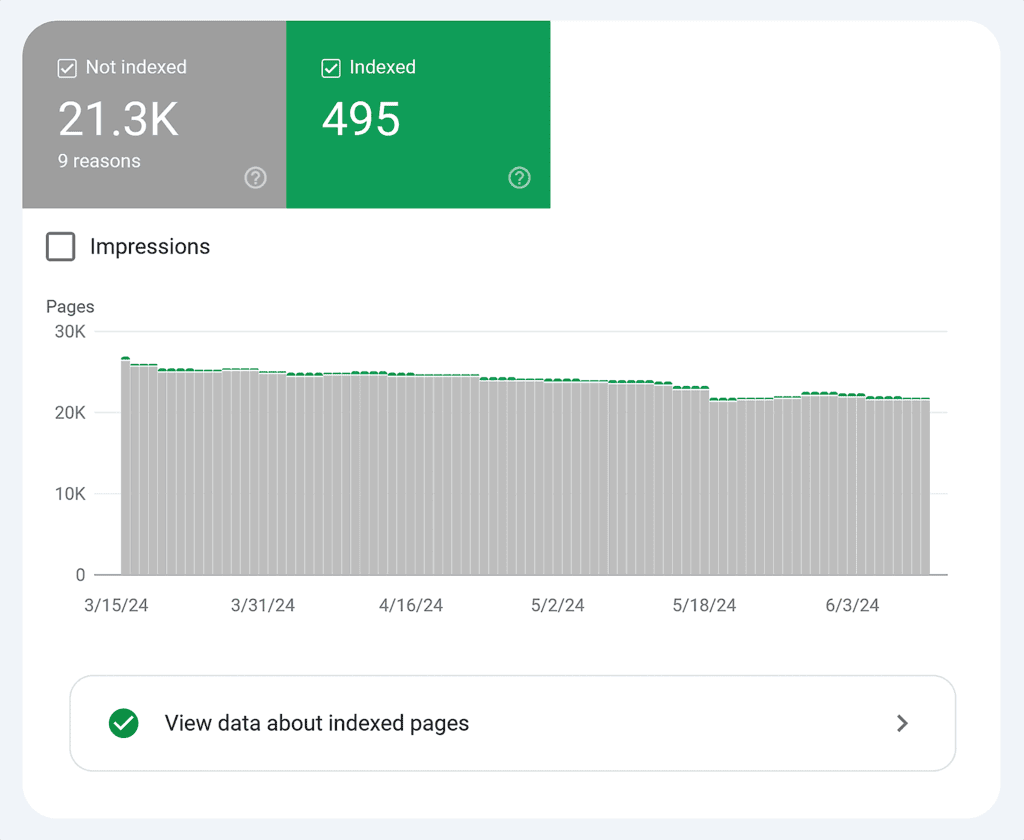
Indexed Pages
Ensure Google is indexing the right pages on your site.
Google Search Console’s Index Coverage report helps you spot indexing issues and track how your content’s visibility grows over time.
Keyword Rankings
Track rankings for target keywords over time to evaluate your SEO strategy’s effectiveness. Use tools like Semrush to see ranking trends, identify content gaps, and find keywords for which you’re gaining or losing ground.
Organic Click-Through Rate
Check your CTR in Google Search Console to understand which pages attract clicks. A low CTR with high impressions suggests you could improve your meta descriptions or titles to better match search intent.
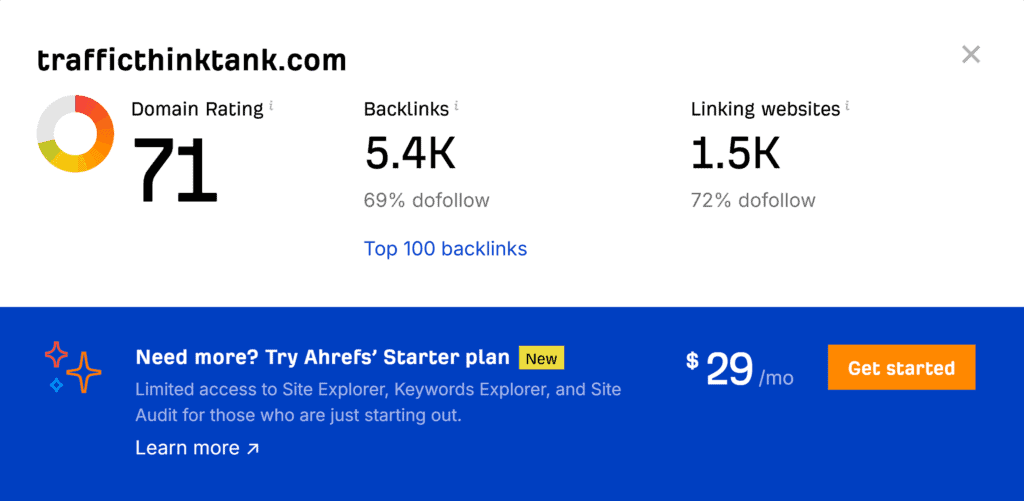
Domain Authority
Use Moz or Ahrefs to track your domain authority and monitor growth as you acquire more quality backlinks. Improving domain authority is a long-term goal but a solid indicator of credibility.
Referring Domains and Backlinks
Regularly audit your backlinks and referring domains. Use Semrush or Ahrefs to identify where new links are coming from, ensuring you’re building a profile with relevant, high-quality backlinks.
5 SEO Blogs You Should Bookmark
Like SEO podcasts, blogs are a great way to stay up-to-date with the latest SEO trends. In my experience, it’s one of the best ways to learn SEO. Also, it’s free.
But if you’ve ever tried to sort through SEO recommendations online, you’ll know how hard it is to find genuinely helpful information.
So, here’s my list of five sites worth checking out because they’re managed by industry leaders and top SEO experts.
1. Traffic Think Tank
Let me start with our Traffic Think Tank blog. We regularly invite prominent industry experts to share their experiences and exclusive insights about SEO in our posts.
For example, my fellow TTT founders, Matthew Howells-Barby (former Hubspot vice president of marketing) and Ian Howells (Head of SEO at The Grit Group), often share their advice and experience on this blog.
If you’re more into video courses, check out our TTT Academy, where industry experts share everything they’ve learned about SEO over the years.
Topics include everything from local SEO to link building to help you level up your knowledge.
2. Search Engine Journal
Search Engine Journal shares news, guides, and expert opinions on SEO-related topics, as well as daily insights about Google, Bing, and other search engines.
It monitors John Mueller’s interviews and social media activity to regularly update SEOs on various SEO-related issues. Moreover, their expert opinion on Google algorithm updates and SEO trends is also worth following.
Reading this blog will help you keep up with new SEO trends, rapid changes in search technology, and how it all affects site owners and SEOs.
3. Backlinko
Backlinko is one of the most valuable resources for learning SEO, offering actionable tips and strategies for SEOs at all stages of their career.
Brian Dean, the founder, along with industry experts, cover essential topics that help you grow your website through well-executed SEO techniques.
You’ll find in-depth guides on keyword research, SEO techniques, link-building strategies, and on-page optimization that go beyond the basics.
You’ll also find tips on technical SEO, such as improving page load times and optimizing for mobile, which are increasingly important for ranking.
On top of that, Backlinko offers tutorials and case studies to help you make measurable improvements in traffic, visibility, and authority.
4. Semrush
Next on my list is the Semrush blog.
It’s a great resource for diving into all sorts of digital marketing topics, like SEO, pay-per-click (PPC), content marketing, email marketing, and social media marketing (SMM).

One thing that sets Semrush’s blog apart is the actionable how-to guides. They don’t just tell you what to do in SEO—they walk you through how to do it using their tools.
So, you’re learning SEO and getting hands-on experience with the Semrush platform at the same time.
5. Neil Patel
Neil Patel’s blog breaks down everything from Google’s latest algorithm changes to advanced optimization techniques in a beginner-friendly way.
You’ll find detailed walkthroughs of keyword research, E-E-A-T implementation, and keyword mapping—all explained through practical examples you can apply to your own site.

What makes this blog particularly valuable is its well-rounded approach to SEO—you’ll stay current with search updates while learning new tips and tricks to increase web traffic.
Frequently Asked Questions about Getting Started with SEO
Now that you’re equipped with the best resources to start learning SEO, I’ve collected a few more popular questions about learning SEO that might interest you.
How can I start learning SEO?
Get started with basic SEO concepts like keyword research, on-page optimization, and backlink analysis.
Many online resources, such as SEO blogs, guides, and tutorials, are available for free. Some resources worth checking out include Traffic Think Tank, Backlinko, Semrush, Search Engine Journal, and Google Search Central, to name a few.
Is SEO easy to learn?
You can grasp SEO basics relatively quickly if you regularly study various online resources, such as expert SEO blogs.
However, becoming an SEO specialist will require gaining hands-on experience, understanding how to do SEO for different websites and niches, and keeping track of the latest updates. It’s a challenging but exciting journey.
Is it possible to self-learn SEO?
Yes, you can self-learn SEO using various online resources. I recommend practicing what you’ve learned by applying SEO techniques to your website or client projects. This hands-on experience will strengthen your SEO knowledge and help you identify areas for improvement.
How long does it take to learn SEO?
Learning the SEO basics can take a few weeks to a few months. However, SEO is an ever-evolving field that requires curiosity, constant learning, and practice. You’ll gain decent SEO experience and confidence within a year or two of consistent hands-on training.
How to Learn SEO and Build the Career You Want
It’s time to skip the guesswork and accelerate your career by learning from top professionals who live and breathe SEO.
Start today with TTT Academy’s course, How to build a successful career in SEO.
TTT Academy offers an extensive library of SEO courses created by industry-leading experts. Inside your membership, you’ll find more than 200 hours of SEO content and monthly Q&A sessions.
And when you sign up for The Full Accelerator plan, you get access to an exclusive Slack community that’s ready to help you through any SEO challenge.
Learn more about joining TTT Academy today.