
Want to improve your SEO rankings and drive more traffic to your website?
You’re not alone.
Over the years, I’ve tested countless SEO strategies—some worked, others fell flat.
But through experience, I’ve found that certain SEO best practices consistently deliver long-term results.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through 20 proven strategies to help your site rank higher, attract the right audience, and convert visitors into customers.
Whether you’re optimizing an existing site or building from scratch, these tactics will set you up for sustained success.
Ready?
Let’s start with the basics: indexable content and a crawl-friendly site.
Ensure Google Can Find & Index Your Content
In my years of working with startups and established companies, I’ve noticed the same SEO mistake—many site owners assume their websites become searchable the moment they hit “publish.”
But SEO doesn’t work that way.
Before a page can rank, it must go through four stages:
Discovering → Crawling → Rendering → Indexing
If your content gets stuck in the first two steps, it won’t appear in search results.
Here’s what you can do to ensure your website gets indexed and ranked.
1. Set Up Google Search Console
Google Search Console (GSC) tells you crucial insights like clicks, impressions, indexed pages, and more.
So, if you don’t have a verified Google Search Account yet, I recommend prioritizing this task.
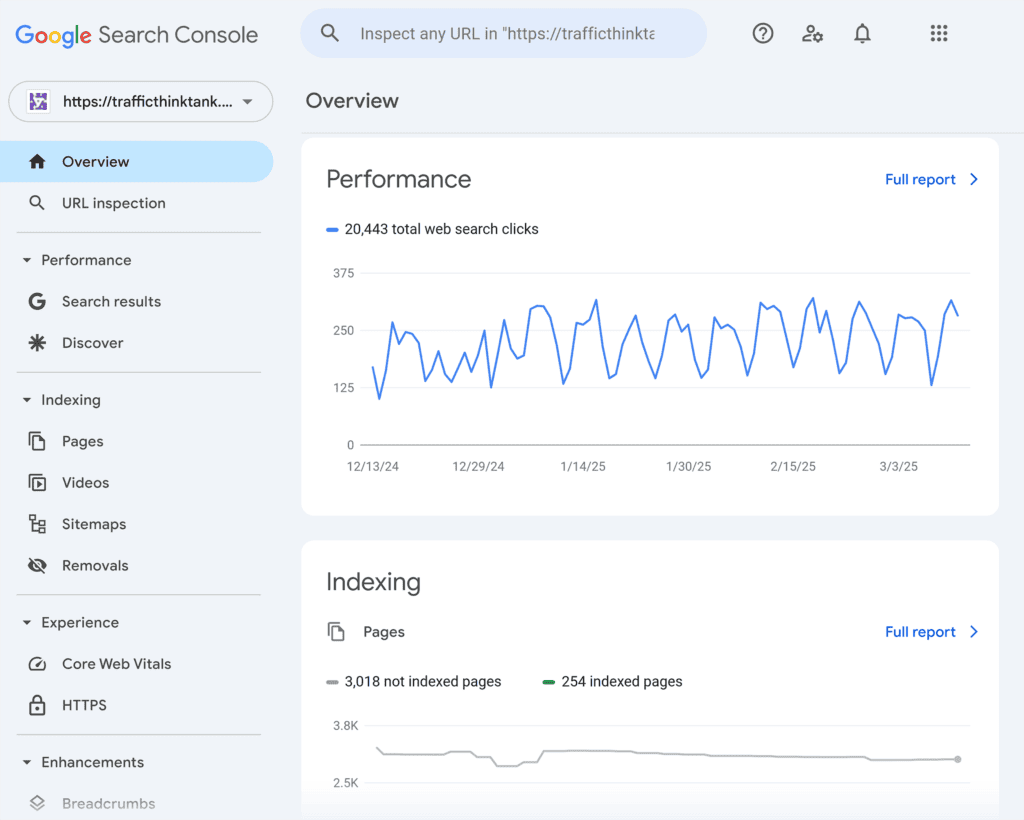
GSC will help you get the most reliable data about your website’s impressions and clicks in organic search results. You’ll also be able to track any technical issues on your website and take prompt action.
Pro tip: Not sure where to start? Read Google Search Console: The Definitive Guide to learn how to set up your account, find and fix indexing errors, and track search performance.
2. Monitor Indexing Issues
Ideally, every webpage that doesn’t have a “No Index” tag should be available on Google.
Some of your website pages might be discovered and crawled by Google Bot but are not added to the Google main index. In this case, users will never find your pages in organic search results because they won’t be searchable.
Monitor your website’s indexing by going to “Indexing” > “Pages” > “Page indexing” in Google Search Console.
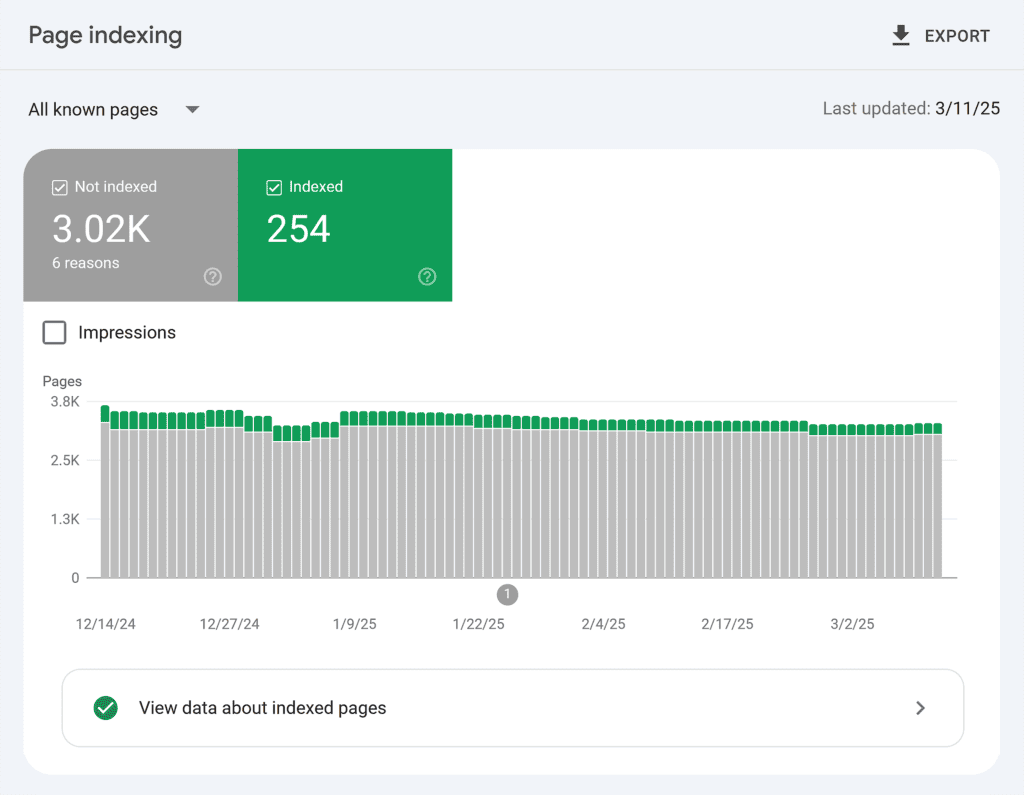
The report also shows you all your indexing errors, if there are any.
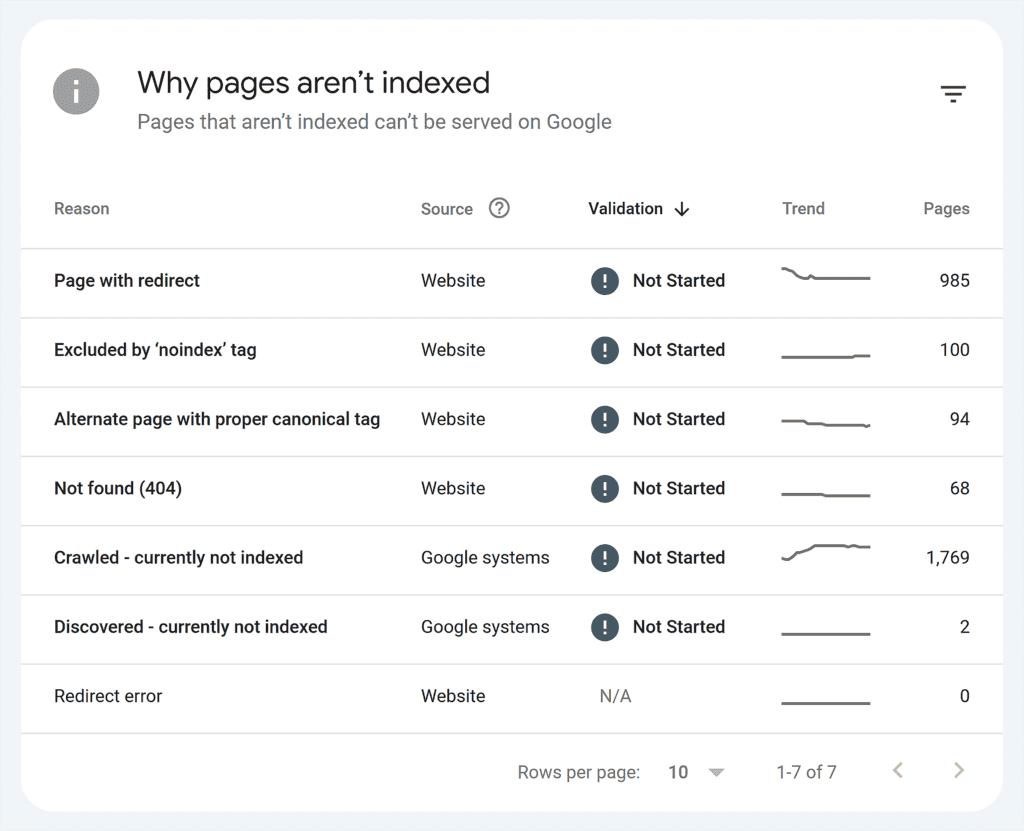
Alternatively, inspect any URL using the Google Search Console search bar.
I recommend paying attention to the following two indexing issues that can occur to recently published pages:
The “Crawled – currently not indexed” indexing issue means a web crawler (such as Google Bot) accessed a particular webpage on your website but didn’t include that page in its index.
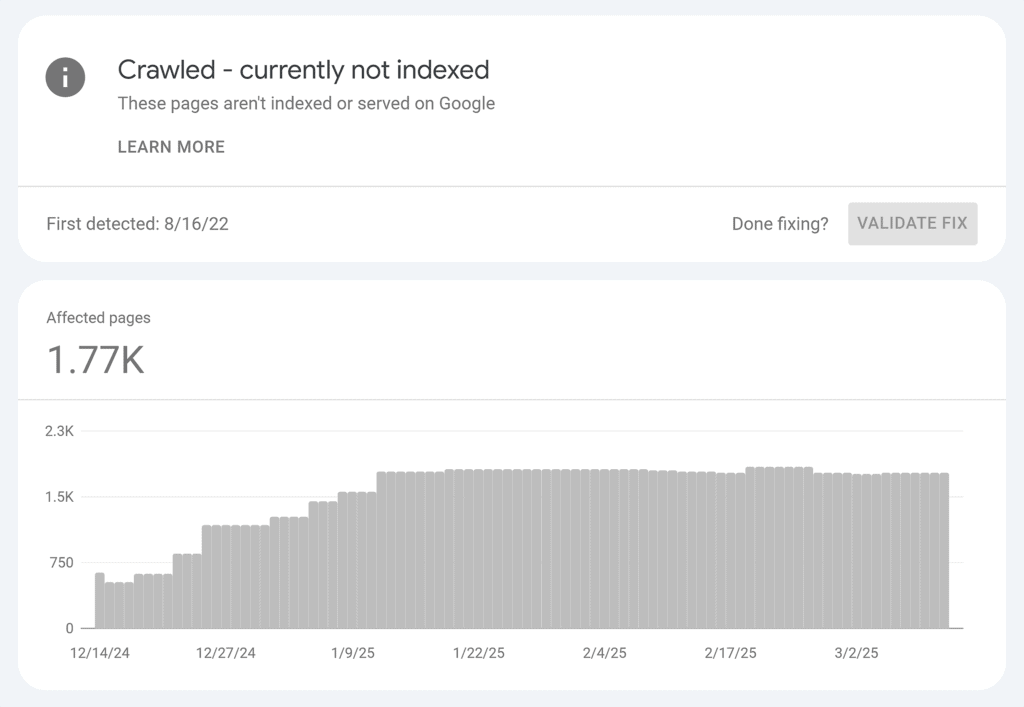
The “Discovered – not indexed” issue means Google discovered your webpage but did not crawl it because the crawl could overload your website. So, Google rescheduled the crawl.
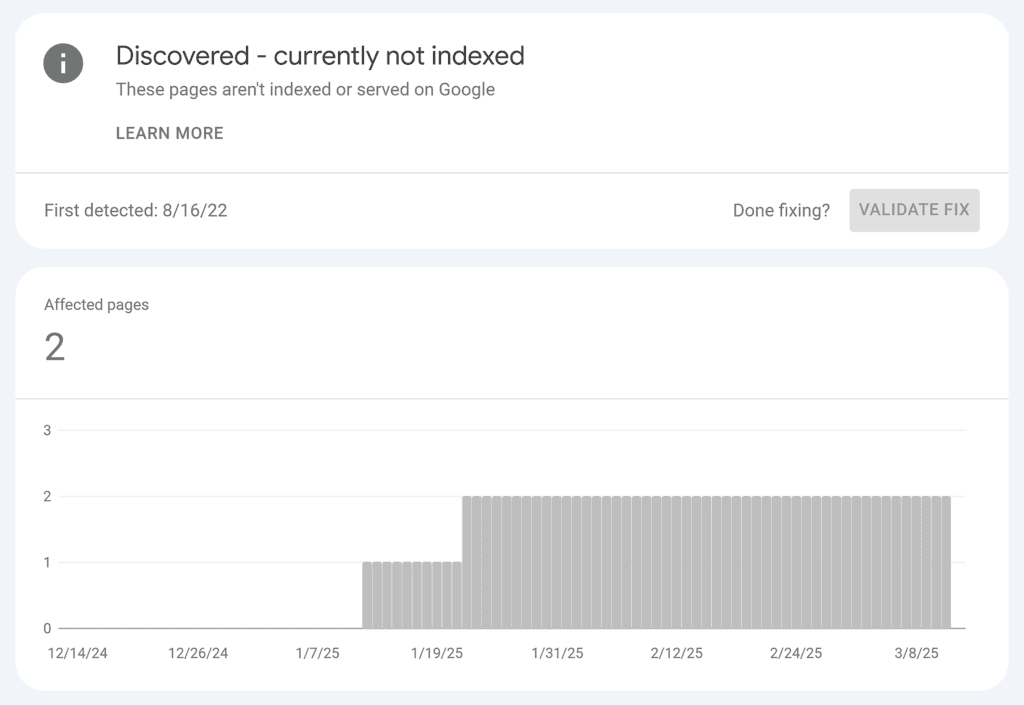
As a best practice for SEO, you’ll want to continually monitor your site for these issues.
Keeping up with your indexing status can help ensure your pages appear in search results faster.
If a page remains unindexed, submit the URL for reindexing to help speed up the process.
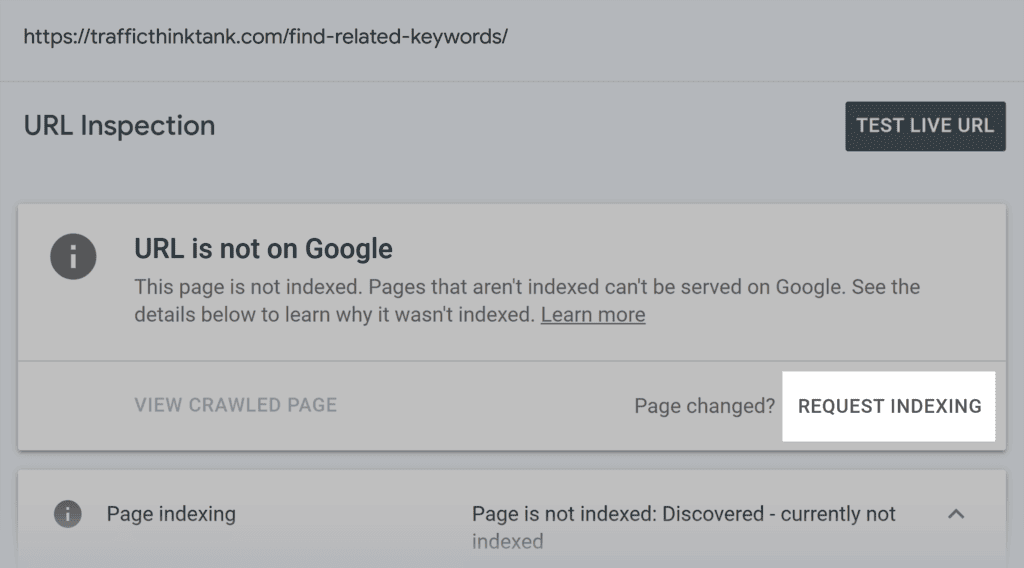
Depending on the issue, you’ll also want to improve internal linking and enhance content quality.
3. Create an XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is essential when it comes to SEO best practices.
Why?
Because it helps search engines see how your website is structured and shows the links between different pages. It also finds orphan pages that aren’t linked anywhere.
Plus, it helps identify pages updated since the last crawl.
All of this makes it easier for search engines to discover and crawl your website.

Some experts say XML sitemaps aren’t mandatory because Google Bots can discover new URLs through internal linking.
But I highly recommend creating one to ensure all important pages are easily found and crawled.
Now, open your website’s homepage and add “/sitemap.xml” to the URL. Can you see a list of URLs?
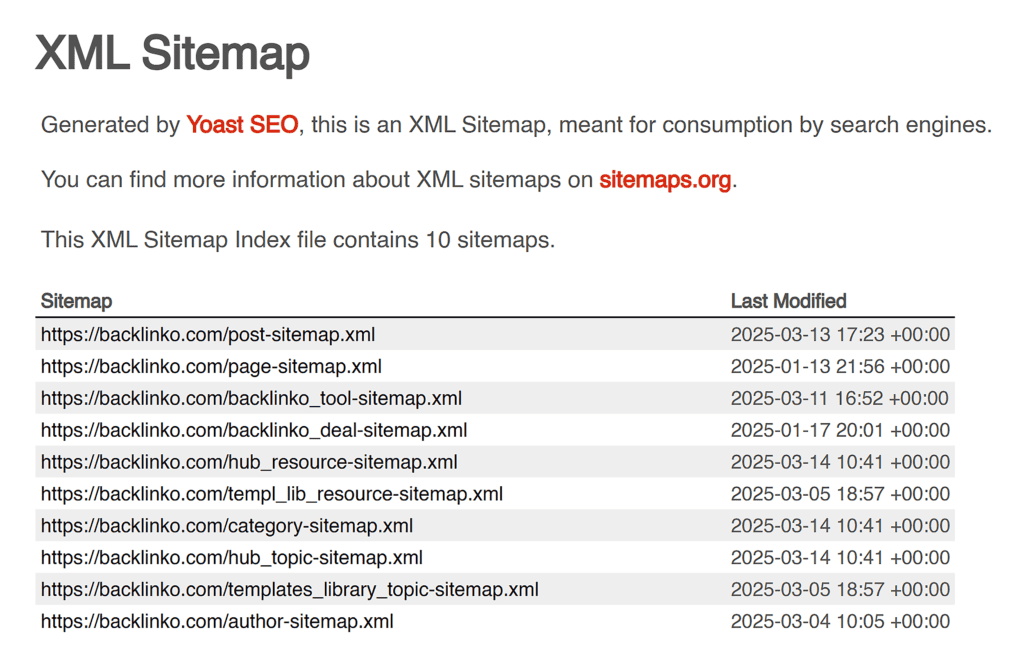
If not, your site doesn’t have a sitemap.
Don’t worry—it’s pretty easy to create one with various tools.
Content management system (CMS) plugins, like Rank Math and All in One SEO, will automatically create an XML sitemap for you.
Alternatively, you can ask a developer to create a sitemap and add it to the root folder of your website.
Once your sitemap is ready, add it to Google Search Console.
Go to “Indexing” → “Sitemaps.” Under “Add a new sitemap,” enter your sitemap URL and click “Submit.”
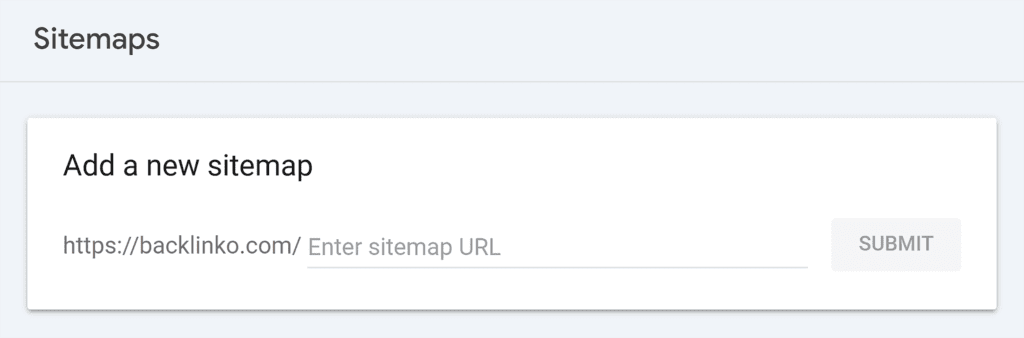
Easy, right? Now, your content will be easier for search engines to find and index.
4. Fix 4xx Errors (if Applicable)
Ever tried to access a webpage only to get an error message?
That’s a 4xx error.
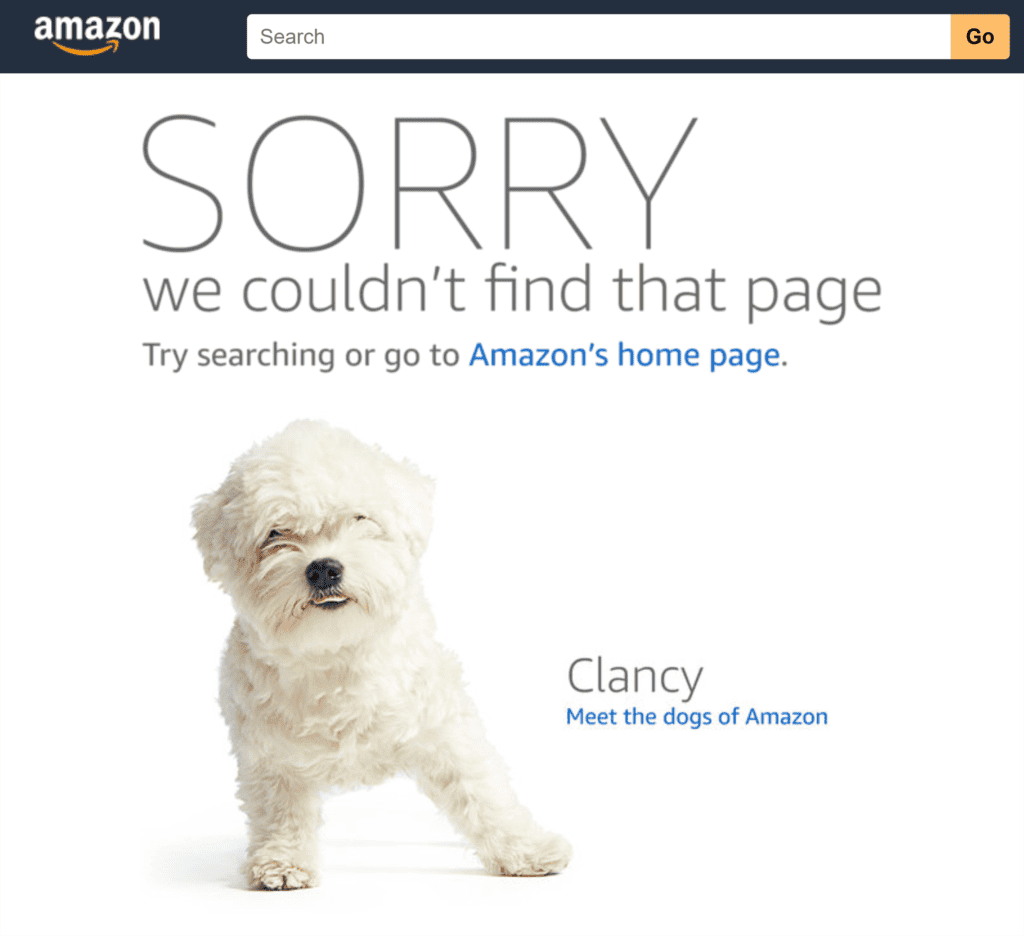
If your website has multiple unresolved 4xx errors, Google may crawl your site less frequently. Over time, these pages could be removed from the index.
The last two digits of the HTTP status codes explain why your webpage isn’t accessible.
- 404: Page not found; its future availability is unknown
- 410: Page permanently removed and won’t be accessible again
If you see a page returning a 4xx error, check Google Search Console to learn more about the issue.
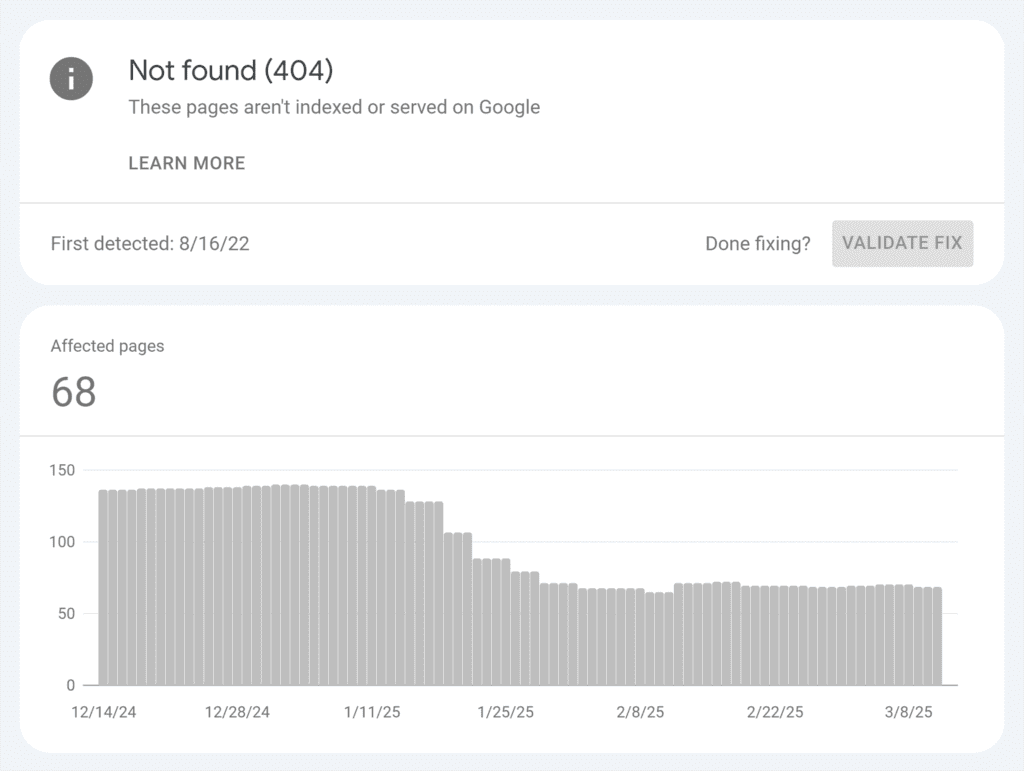
Restore the page, set up a redirect, or update the URL as needed.
Pro tip: Use a site audit tool to get notified automatically about 4xx errors and other website errors to help improve your rankings.
5. Create a Robots.txt File
Robots.txt is a text file that tells search engine bots which pages they can crawl.
If you want to block certain areas—like test environments, client dashboards, or WordPress admin panels—you can do it with robots.txt.
This helps prevent crawlers from wasting their budget.
While it’s not mandatory, I highly recommend using a robots.txt file to control what gets crawled.
Note: Robots.txt only controls crawling, not indexing. If a blocked page is linked somewhere else, search engines can still index it. To keep a page out of search results entirely, use a “noindex” setting instead.
Not sure whether your website has a robots.txt file?
Add “/robots.txt” to your website’s URL.
If it does, you should see something like this:
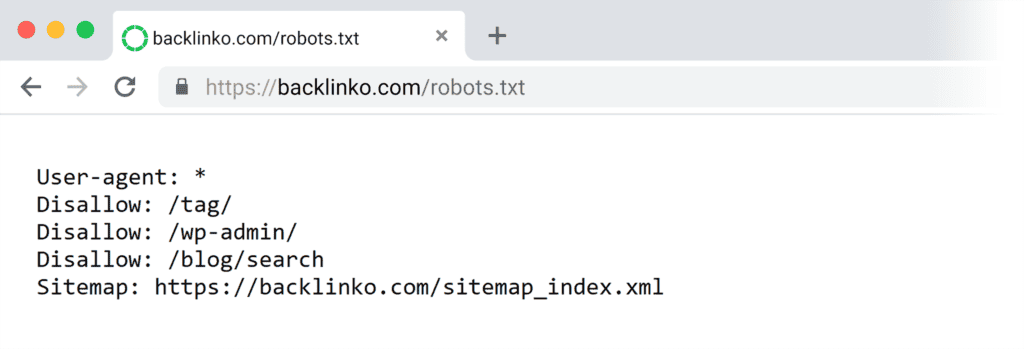
If it doesn’t (and you want to create a robots.txt file), you can do so easily with a plugin like Yoast SEO or All in One SEO.
Speed Up & Structure Your Site for Better Rankings
Search engines—and users—favor websites that load fast and are easy to navigate.
A slow, poorly structured site won’t just frustrate visitors; it can also limit your rankings and make it harder for search engines to crawl and understand your content.
By improving technical performance and site architecture, you create a seamless experience that boosts engagement and strengthens your SEO foundation.
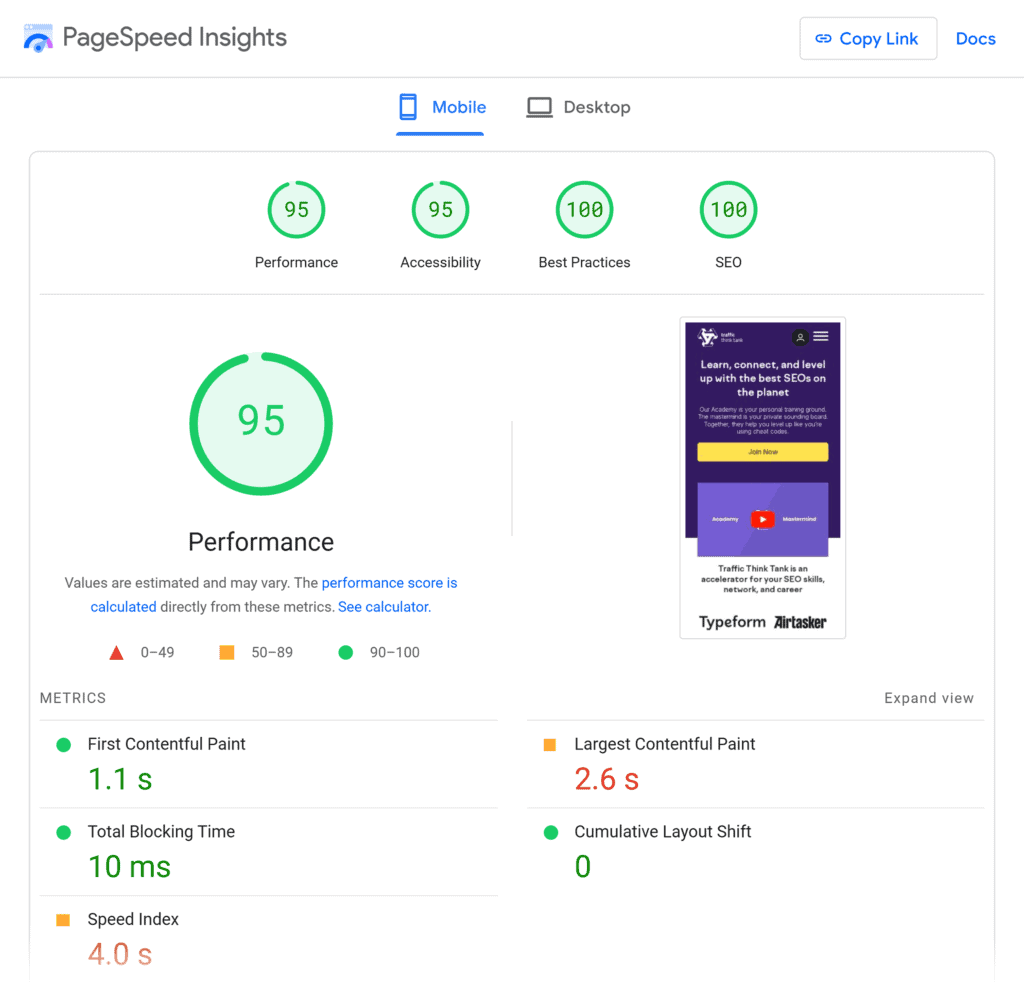
6. Improve Page Loading Speed
According to Google, page loading speed is one of the user experience metrics that impact rankings.
Your website pages should load quickly enough to ensure a smooth on-site user experience.
Since many searches happen on mobile, optimizing for mobile performance—like responsive design and mobile-friendly layouts—is crucial for maintaining rankings and engagement.
Improving page speed isn’t just a technical fix; it’s an SEO best practice that enhances user experience and search visibility.
Whether you launch a new website or conduct an SEO audit of an existing website, use the PageSpeed Insights tool developed by Google to check page loading speed and get improvement recommendations.
7. Optimize URLs
Google recommends using short and descriptive URLs that convey essential information about a webpage and its content for users and search engines.
- Good URL structure example: site.com/art-canvas-print
- Bad URL structure example: site.com/index.php?id_sezione=360&sid=3a5ebc944f41d
I’m sure you’ve seen poor URL structures a few times when browsing the web.
They’re long, unfriendly, and confusing. Whenever I see such a page loading, I often think it’s spam.
So, ensure your website settings let you customize URL slugs.
I also recommend including your target keyword in the URL slug. It’s not a strong ranking factor, but it will help Google better understand what your webpage is about.
Pro tip: Want to learn more about keywords and how to find them? Check my in-depth article about the importance of keywords for SEO.
8. Include Internal Links
Internal links help search engines understand your site’s structure and distribute link equity across your pages. They also enhance user experience by guiding visitors to relevant content and keeping them engaged longer.
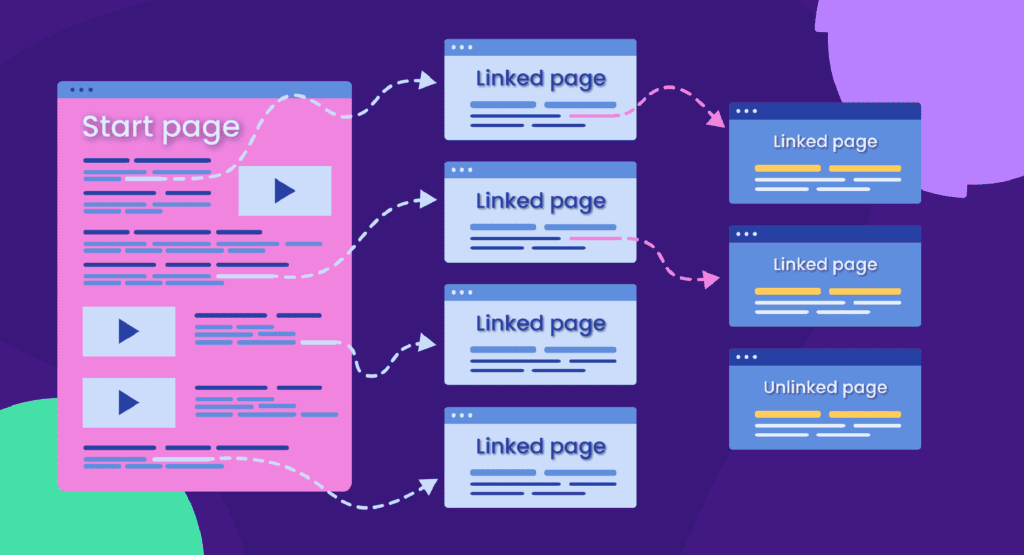
To maximize their impact, follow these best practices for internal linking:
- Link to high-priority pages: Direct users to your most valuable pages, such as service pages, product pages, or cornerstone content
- Use descriptive, keyword-rich anchor text: Instead of generic phrases like “click here,” use text that clearly indicates what the linked page is about
- Ensure a natural flow: Internal links should feel organic within the content, not forced
- Avoid excessive linking: Too many links in a single section can overwhelm users and dilute their impact
- Regularly audit internal links: Check for broken links, outdated pages, or missed opportunities to link to newer content
By optimizing your internal linking strategy, you improve site navigation, enhance SEO, and distribute link equity more effectively.
9. Use Structured Data Markup
Schema (also known as structured data) is code you add to webpages to help search engines like Google and Bing understand your content.
Implementing structured data is one of the best SEO practices to help search engines better understand your website content.
It can also lead to enhanced search results and rich snippets in SERP features.
Like reviews, star ratings, FAQs, and more.
If you’re tech-savvy, you can manually write code using Schema markup.
Alternatively, you can use plugins to generate Schema for you automatically:
- Yoast SEO: Automatically adds structured data for blog posts, articles, and breadcrumbs
- Schema Pro: A user-friendly plugin that supports various schema types, including reviews, FAQs, and events
- Rank Math: A powerful SEO plugin that includes built-in schema generation for different content types
- Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper: A free tool to help generate structured data without coding
Start with FAQ, Product, Event, Rating, or How-To structured data to improve your site’s search presence and enhance SERP features.
I recommend setting up structured data for a new webpage before publication or updating existing content.
Based on my experience, Google displays rich snippets a few days after updating content for webpages ranking in the top 10 organic search results.

Optimize Your Site for Higher Search Visibility
When it comes to SEO best practices, high-quality content is non-negotiable.
But you also need to structure your site and strengthen its authority. This will help search engines recognize its value and allow users to find it easily.
By refining key on-page elements, you increase your chances of ranking higher and attracting more clicks.
10. Align Your Content with Search Intent
Search intent is the “why” behind a user’s query.
In other words, it’s the purpose they have in mind when searching.
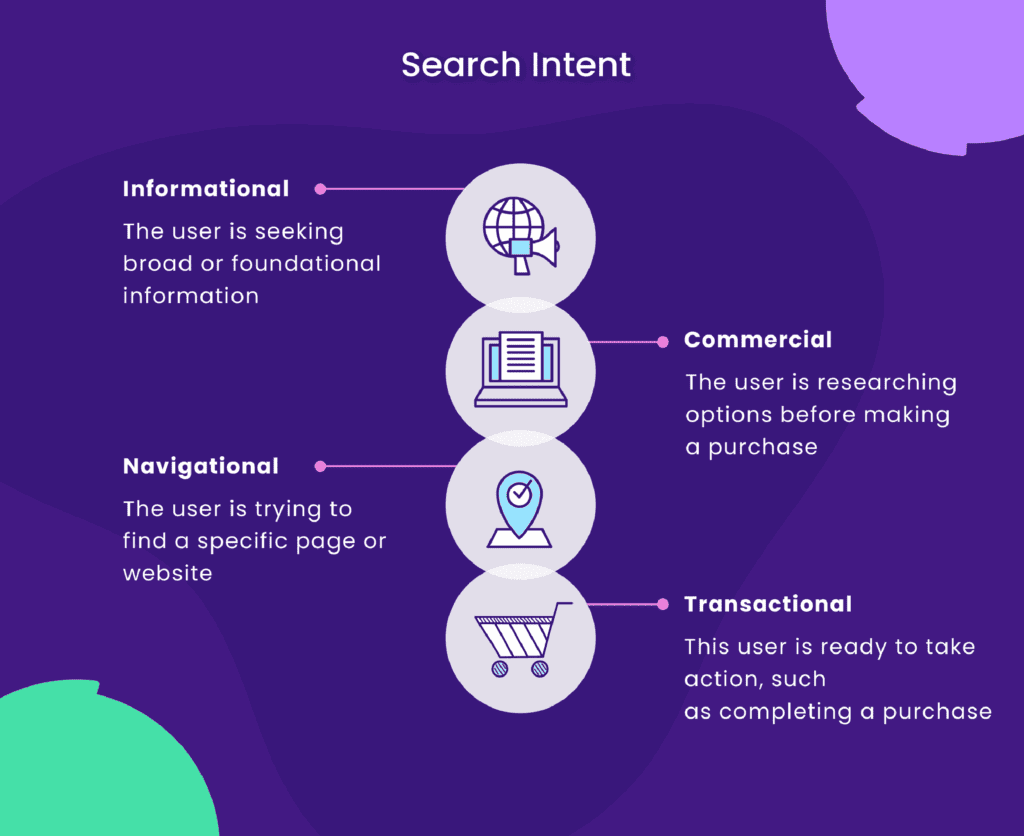
There are four types of search intent you should know:
- Informational: Users want to learn something (“how to optimize images for web”)
- Navigational: Users are looking for a specific website or page (“Facebook login”)
- Transactional: Users want to complete an action or purchase (“buy iphone”)
- Commercial: Users are researching before making a purchase decision (“best SEO tools”)
Aligning content with search intent is essential for delivering value to users and increasing engagement.
This is why I always recommend analyzing search engine result pages (SERP) for the target keyword to understand and align your content with users’ search intent.
Tools like Semrush’s Keyword Overview can also help by identifying search intent for keywords and related terms.
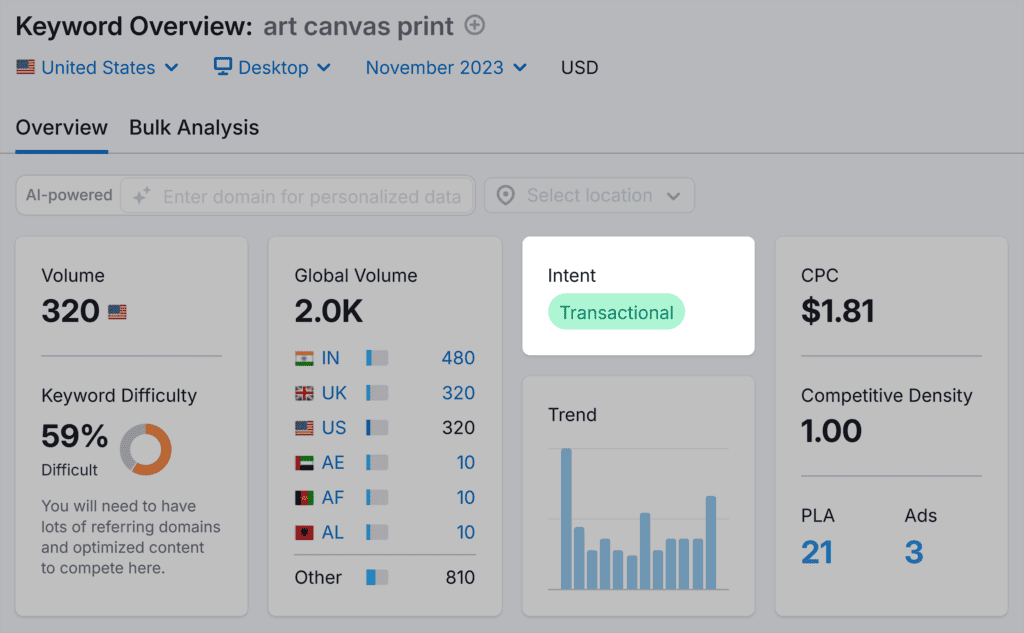
Once you know the search intent of a keyword, you can select the appropriate content type to ensure it matches.
For example, if it’s an informational keyword, comprehensive guides work well.
For transactional queries, focus on product pages with clear calls to action. For commercial, comparison posts and reviews perform better.
11. Use On-Page Optimization Strategies
An essential factor for your website’s organic growth is on-page optimization.
Despite the rumors that SEO is dead and keyword targeting no longer works, it’s as important as it used to be. The impact of SEO is phenomenal if you follow proven-to-work strategies.
Whenever you work on new content for your website that needs to rank on Google, follow these on-page SEO strategies:
- Identify relevant keywords and phrases for your content
- Create high-quality, informative, and engaging content
- Optimize your title tags with target keywords
- Write compelling meta descriptions to make users click (keep reading to learn how to do it)
- Use header H1 tags (plus H2 and H3) to structure content and include keywords
- Link to related pages within your website for better user navigation
- Choose your outbound links wisely
- Optimize images with descriptive filenames and alt tags
- Create clean, descriptive URLs with keywords where applicable
Further reading: The Future of SEO: Key Trends and What to Expect
12. Publish High-Quality Content
Since ChatGPT’s introduction in 2022, many website owners have turned to AI tools for content creation.
While AI can be a powerful asset, many use it to mass-produce low-quality content, hoping to game search rankings.
In response, Google has refined its algorithms, rolling out updates like the Helpful Content Update to prioritize valuable, well-researched, and user-focused content.
To grow your website in organic search results, I recommend complying with Google’s content quality guidelines.
These include Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T) and Your Money or Your Life (YMYL), which help ensure your content is accurate, reliable, and valuable to users.

To align with E-E-A-T and YMYL guidelines:
- Demonstrate expertise: Provide well-researched, accurate content backed by real-world experience
- Showcase authority: Include author bios, credentials, and links to reputable sources
- Build trust: Use clear, transparent information and avoid misleading claims
- Keep content updated: Regularly refresh posts to reflect the latest insights and best practices
Keeping E-E-A-T and YMYL in mind doesn’t mean you can’t use AI-generated content, though. It simply means your content should reflect your expertise, experience, authority, and trustworthiness whether or not you use AI generation tools.
13. Optimize for Featured Snippets
A featured snippet is a small block of text that appears at the top of Google search results—often called “position zero” because it ranks above the first organic result.
Snippets can take the form of short definitions, lists, tables, or step-by-step instructions.

Optimizing for featured snippets can boost visibility and clicks, even if your page isn’t in the top three positions.
Increase your chances of securing a featured snippet with these tips:
- Identify snippet opportunities by analyzing search results for your target keywords
- Format content properly using clear headings, bullet points, and concise summaries
- Provide direct answers in the first few sentences of a section
- Use structured data to help Google understand your content’s relevance
14. Build High-Quality Backlinks
Backlinks remain one of the strongest ranking factors in SEO. Earning links from reputable websites signals to Google that your content is valuable and trustworthy, which can boost your rankings and drive referral traffic.
However, not all backlinks are created equal.
To build strong backlinks, focus on the following:
- Prioritize quality over quantity. Links from authoritative, relevant sites carry more weight than a high volume of low-quality links.
- Create link-worthy assets, like infographics or original research
- Leverage digital PR, such as newsworthy reports and expert commentary
- Engage in broken link building by replacing dead links with relevant content
- Try guest blogging on authoritative industry websites
Pro tip: Build a strong backlink profile by learning who’s linking to you (and your competitors) with our free backlink checker.
Increase Your Click-Through Rates & Engagement
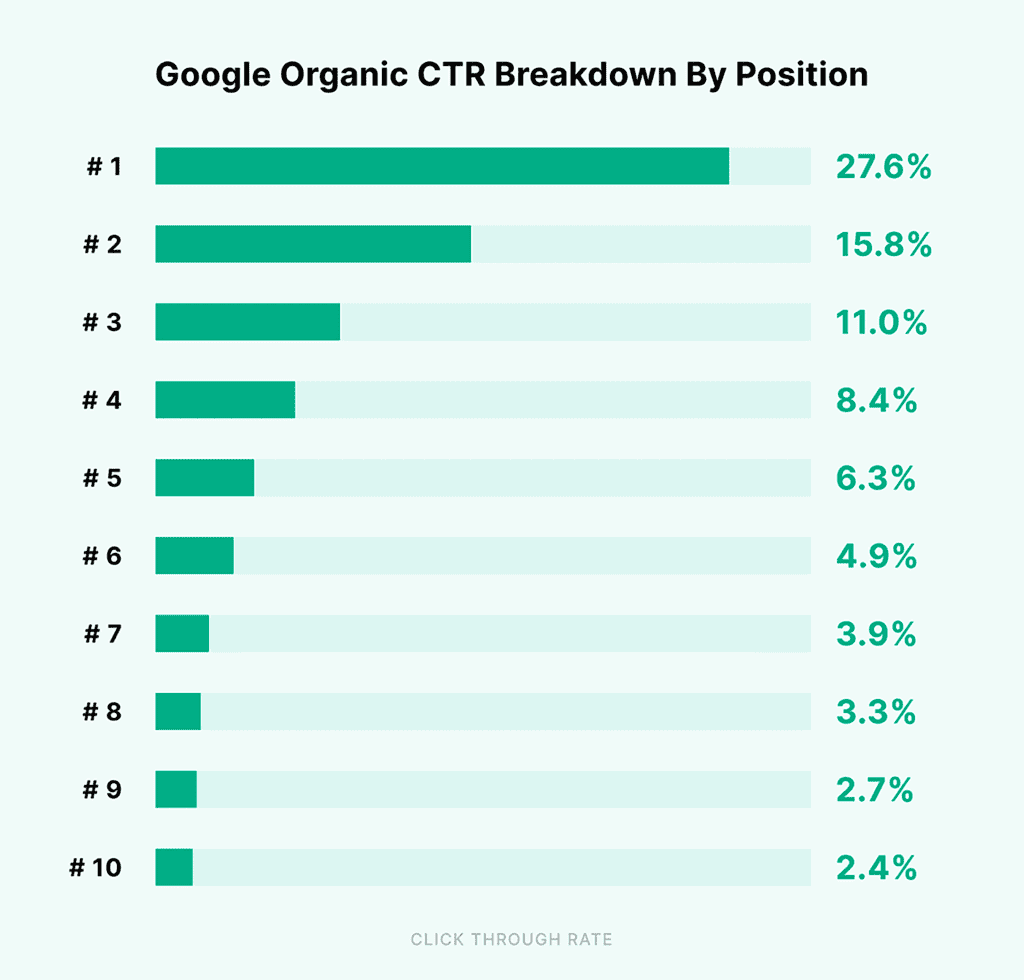
Ranking on Google is only half the battle—getting users to click is just as important. Your click-through rate (CTR) determines how often people choose your result over others.
For instance, Backlinko analyzed four million Google search results and discovered that the top five spots account for over 69% of all clicks.
In other words, most users’ attention is directed to the top five results on Google.
If users come across your webpages in organic search results but don’t click, implement the SEO best practices I describe below to make your website stand out.
14. Write Click-Worthy Meta Titles
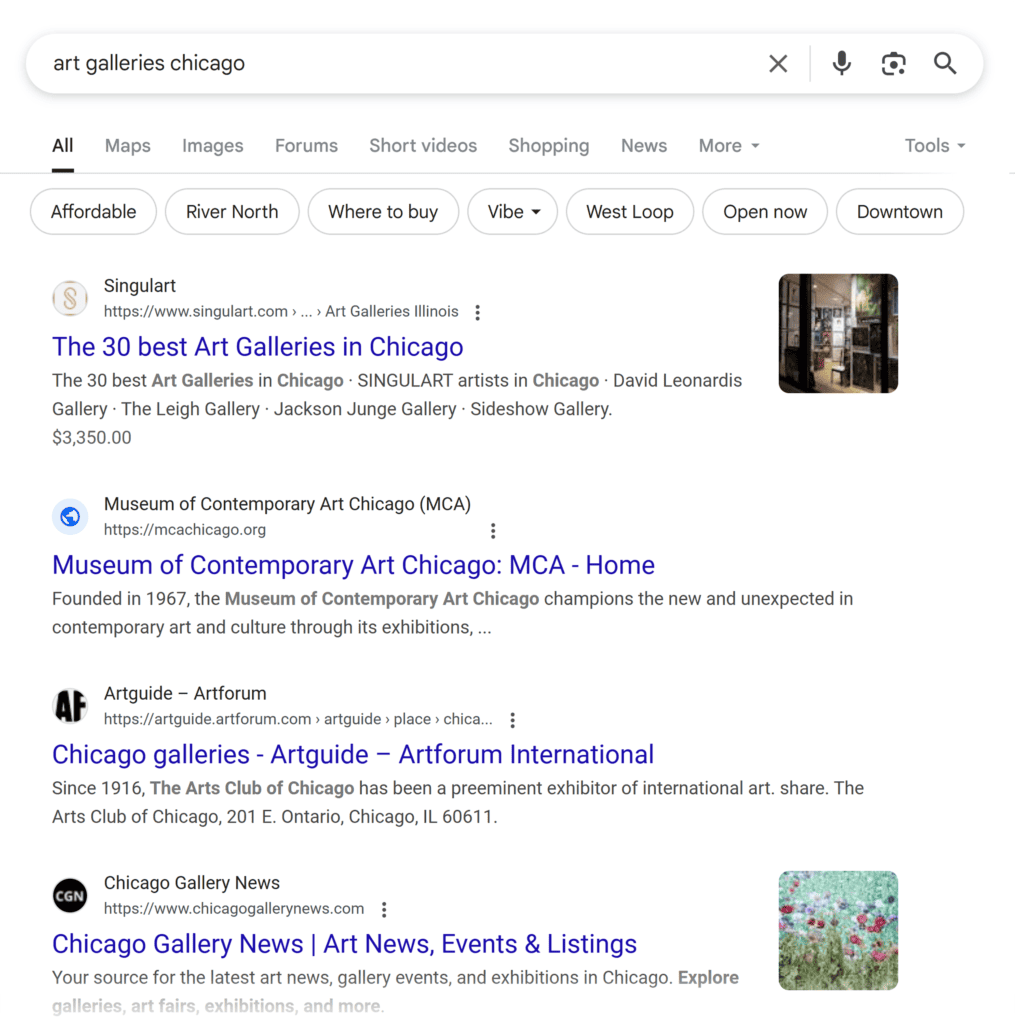
Before creating a meta title for your webpage, do a competitor website traffic analysis to review who’s already ranking in the top 10…and how catchy their metadata is.
For example, if you Google “art galleries in chicago,” you’ll see that most organic search results look pretty similar.
Now, imagine you’ve created the following meta title for your webpage: “3 Art Galleries in Chicago to Visit in One Day.”
Doesn’t that feel more engaging?
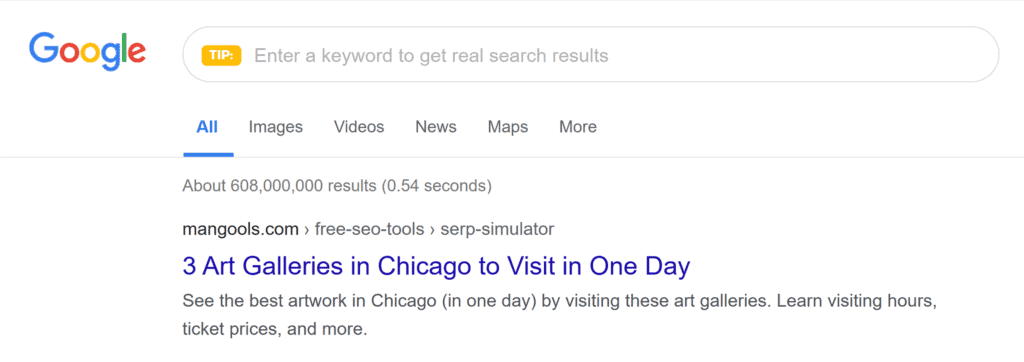
A well-crafted meta title like this can help your page stand out and attract more clicks. But to be effective, it needs to be concise and compelling.
Google typically displays only the first 600 pixels (about 50-60 characters) on mobile before truncating it, so keeping it short ensures your full message is seen.
You can also use power words in your meta titles to drive action, trigger emotions, and help users relate to your brand before visiting your website.
This includes:
| Secret | Elevate | Crush | Surge |
| Discover | Dominate | Win | Explode |
| Amplify | Ignite | Accelerate | Fast-Track |
| Master | Unleash | Maximize | Command |
| Ultimate | Breakthrough | Skyrocket | Outperform |
| Revolutionize | Transform | Conquer | Next Level |
| Unlock | Exclusive | Optimize | Game Changer |
| Achieve | Turbocharge | Definitive | Iconic |
These words create a sense of curiosity, urgency, and value. I recommend using them strategically to make your meta title more appealing to users.

Another trick for making your title tags stand out? Include numbers for specificity.
By including numbers, you make your meta title more specific, actionable, and catchy compared to your competitors.
If most search results are text-heavy, adding numbers will help attract users’ attention and communicate the value they’ll get from reading your content.
Here’s how you can include numbers in a meta title:
- A list of actionable items (for checklists or how-to guides)
- The number of items from a listicle
- The number of products and prices (for ecommerce websites)
- The year of publication or when you updated it to show that your content is fresh
15. Craft Compelling Meta Descriptions
Your meta description should reinforce your title and persuade users to click. It’s not just a summary—it’s a pitch.
For example, instead of “This post covers how to rank higher on Google,” you could say:
“Learn exactly how to beat Google algorithms for higher rankings. Includes free resources, practical strategies, and case studies.”
Why does it work?
This approach highlights specific benefits (“beat Google algorithms”), offers tangible resources (“free resources, practical strategies”), and provides social proof (“case studies”).
By addressing what readers will gain and how they’ll get it, you create both curiosity and confidence in your content’s value—compelling elements that drive higher click-through rates.
Pro tip: Include your primary keyword in your meta description. This shows searchers your content is a perfect match for their query and can increase your click-through rate.
To ensure your full message appears in search results, keep it within Google’s recommended length of about 680 pixels (roughly 120 characters on mobile).
Similar to title tags, Google will truncate meta descriptions that are too long. This can cut off important details, reducing their effectiveness.
Convert Traffic into Paying Customers
The ultimate goal of launching and growing a website is profit, right?
The following SEO best practices are organic conversion rate optimization (CRO) strategies that worked well for me in the past years of my SEO career.
16. Use Enticing CTAs
Want more conversions? Make your calls to action (CTAs) clear and strategic.
Here’s how:
- Include a CTA in every piece of content: If you don’t ask your audience to take action, they’re less likely to do so
- Use button CTAs on landing pages: Clear and actionable copy works best
- Add in-text CTAs to blog posts: Internal linking improves SEO and keeps users engaged
- Stick to one CTA copy on landing pages: Multiple CTAs can confuse users
- Encourage specific actions: Ask your audience to buy a product, fill out a form, download a lead magnet, or subscribe to updates
For example, Semrush uses a mix of CTAs in its blog content, ensuring they’re related to the article’s topic.
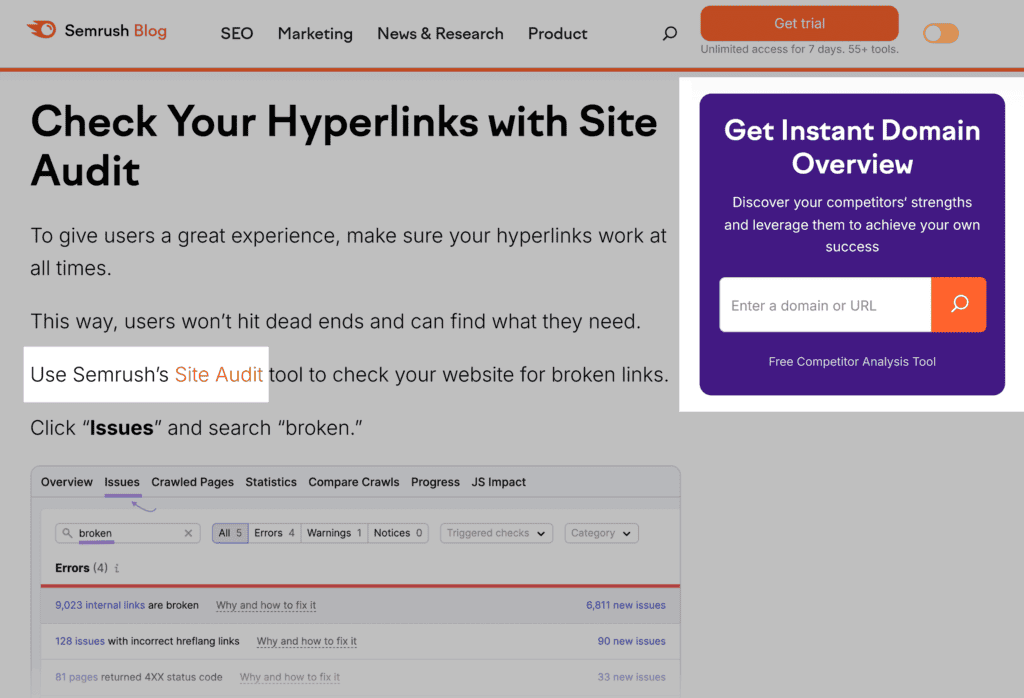
17. Customize Offers According to Search Intent
If your audience is still researching, they aren’t ready to buy—no matter how many CTAs you use.
To get results, focus on why they’re searching. Their intent should guide what you offer, not the other way around.
Create a marketing funnel that matches their decision-making process.
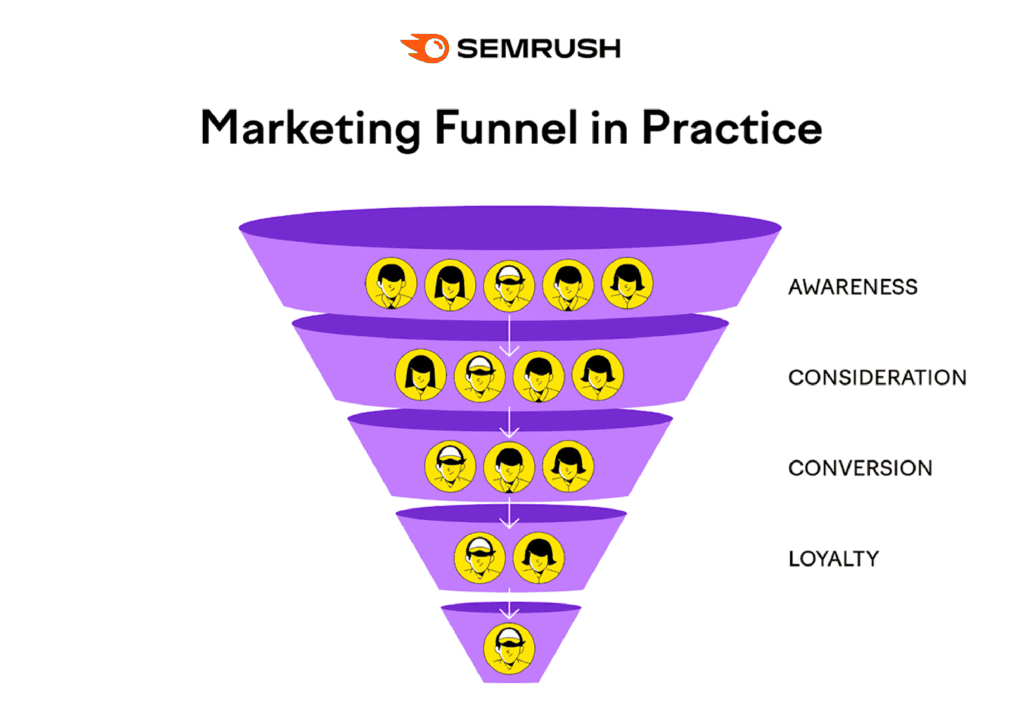
In the early stages, most people are looking for information, not a sales pitch. Use educational content to build trust and guide them toward the next step.
To keep them engaged, encourage actions like:
- Download a lead magnet
- Read reviews
- Subscribe to your newsletter
- Try a product demo
- Sign up for a free trial
This isn’t a sale yet, but it moves them closer.
When they’re ready to convert, send them to a landing page designed to close the deal. This approach works because it follows how people naturally make decisions.
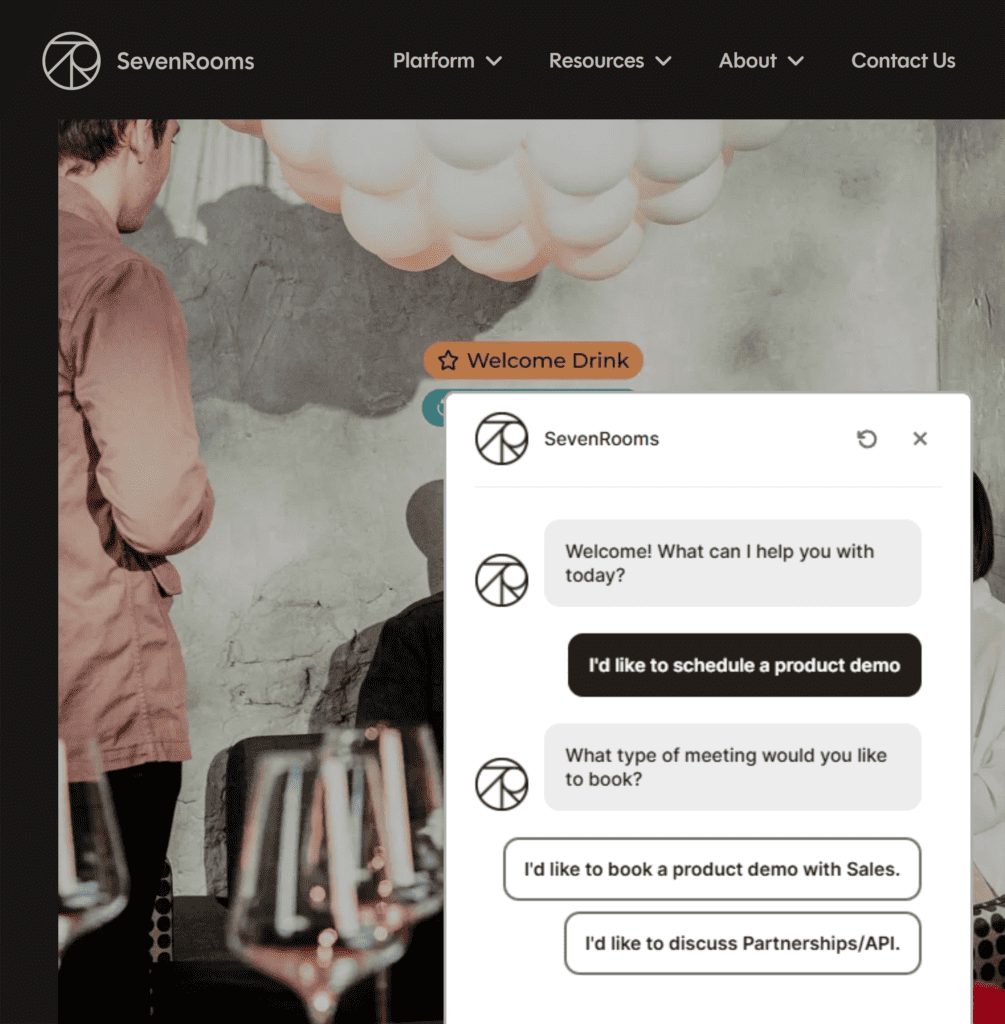
18. Add Chatbots to High-Performing Pages
I once experimented with a chatbot on a B2B lead generation page—the results were impressive.
Instead of asking people to fill out a form and wait for someone to contact them, we added a chatbot to the lead generation page to answer users’ questions and address their concerns immediately.
And people loved it.
It helped make a conventional page interactive and engaging, generating more leads for the client.
You can also use chatbots to:
- Qualify leads by asking pre-screening questions
- Schedule meetings without back-and-forth emails
- Provide instant support to reduce bounce rates
- Offer product recommendations based on user input
- Book product demos
19. Leverage Lead Magnets
I’ve already mentioned lead magnets as a CRO strategy related to SEO best practices.
Lead magnets are incentives or valuable resources you can offer your target audience in exchange for their contact information, usually their email addresses.

The primary goal of lead magnets is to attract potential customers, nurture them, and eventually convert them into paying customers.
Based on my experience, ebooks with industry trends, how-to guides, and checklists help collect users’ contact information that you can later use for email marketing.
For example, Semrush has a powerful lead magnet strategy. They offer free online marketing courses where you learn the subject using Semrush tools in exchange for signing up for a free account.
This way, Semrush shows the value of its toolkit and attracts new customers.
20. Conduct A/B Tests
I’m sure you’ve heard of A/B testing, also called split testing, as one of the “old school” CRO strategies. It’s effective because you compare two identical webpages where only one element differs, such as a CTA copy, a button placement, a headline, etc.
This lets you quickly identify what resonates best with your target audience.
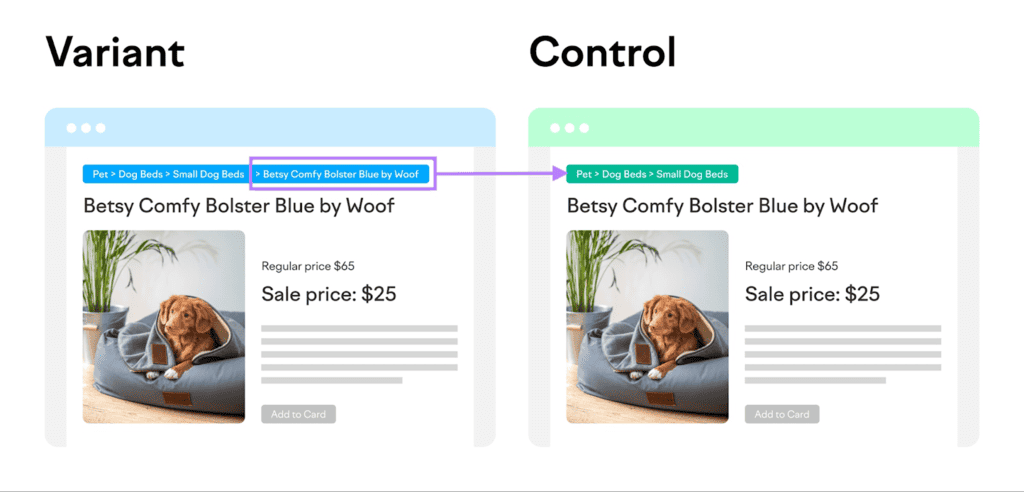
So, you can boost impressions, click-through rates, and leads.
Note: Your website should get substantial monthly organic web traffic to get statistically significant results.
Common SEO Myths Debunked
The world of SEO is full of misinformation and outdated tactics. As search engines evolve, so too must our strategies.
Let’s clear up some of the most common misconceptions about SEO and explain why they no longer hold up.
Myth #1: More Keywords = Higher Rankings
Some still believe stuffing content with keywords will boost rankings. In reality, Google’s algorithms focus on relevance and quality rather than sheer keyword density.
Overusing keywords can actually harm rankings, as search engines may flag the content as spammy.

Instead, focus on natural language, search intent, and strategic keyword placement for the best results.
Myth #2: Longer Content Always Ranks Higher
It’s true that in-depth content often performs well, but word count alone isn’t a ranking factor.
Google prioritizes content that fully answers the user’s query, whether it’s 500 words or 5,000.
So, focus on creating valuable, well-structured content rather than stretching it just to hit a word count.
Myth #3: Domain Age Is a Major Ranking Factor
Older domains don’t automatically rank higher than newer ones. Google prioritizes relevance, authority, and content quality over age.
A well-optimized, content-rich website can outperform an older domain that lacks valuable content and strong backlinks.
Myth #4: More Links Mean More Authority
Many website owners assume getting more backlinks automatically improves rankings, but not all links are valuable.
Low-quality, spammy backlinks can harm your site more than help, potentially triggering Google penalties and reducing your credibility.
For example, here’s a backlink audit highlighting toxic and potentially harmful links. If left unchecked, these could negatively impact rankings and trust.
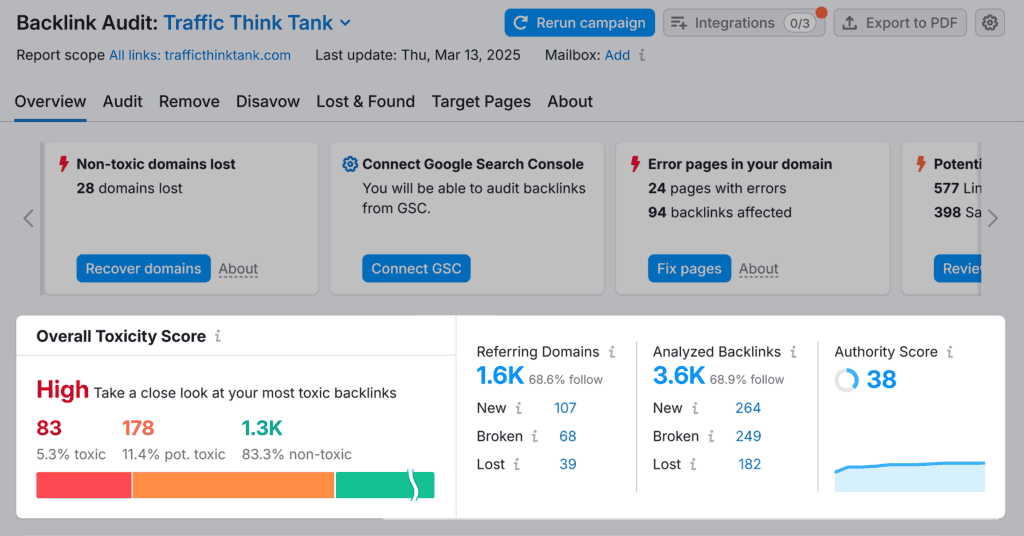
Focus on earning high-quality, relevant links from authoritative sources through guest posting, digital PR, and content that naturally attracts backlinks.
Myth #5: Meta Descriptions Directly Impact Rankings
While meta descriptions don’t directly influence rankings, they play a huge role in CTRs.
A compelling description can attract more clicks, which can indirectly improve rankings by signaling to Google that your page is relevant.
Writing engaging, accurate descriptions is an SEO best practice that can help increase your organic traffic.
Master SEO Best Practices to Outrank Your Competition
Implementing SEO best practices is just the beginning—staying ahead requires ongoing learning and strategic execution.
If you’re ready to refine your approach and tackle advanced SEO challenges, check out Traffic Think Tank Academy.
It’s packed with expert-led courses and real-world strategies to help you drive measurable results.
Explore TTT Academy today and take your SEO skills to the next level.
Semrush
- Semrush – Best overall SEO functionality
- Google Search Console – Best free (partial) data from Google
- Advanced Web Ranking – Best for reporting
- SERPWatcher by Mangools – Best for bloggers and small teams
- Ahrefs – Best for keyword analysis
- SEO PowerSuite – Best affordable option
- SEO Monitor – Best for forecasting
- Local Viking – Best for local SEO map tracking
- Nozzle – Best for data visualization
- ProRankTracker – Best for agencies and SEO professionals