
Internal linking might feel like busy work, but it’s far from it.
Every link you add helps users discover your content, tells Google what matters on your site, and keeps visitors engaged longer.
It can also boost your site’s overall SEO performance.
In this guide, I’ll teach you seven internal linking best practices that will improve your site’s performance and user experience.
Useful resource: Download our internal linking checklist so you can audit your current approach and make immediate improvements.
Let’s start with why internal linking is so important.
Why Internal Linking Matters for SEO
Internal linking remains a foundational element of technical SEO that directly impacts how search engines crawl, understand, and rank your content.
Here’s what it can do for your site:
- Facilitate Google indexing: Google’s crawlers use internal links to discover and index new content, and effective linking strategies lead to faster, more accurate indexing
- Distribute authority to internal pages: By linking effectively, you can pass authority from your homepage (or other popular pages) to your internal pages. This interconnectedness helps you improve overall search rankings.
- Boost SEO: Internal links with keyword-rich anchor text add value and help you rank higher in search results and SERP features
- Add value for visitors: By connecting relevant content, you enhance the user experience, encourage longer site engagement, and build trust

Now, I’ll cover seven internal linking best practices for creating a user- and search-engine-friendly site.
1. Mix Up Your Anchor Text
To maintain a natural link profile, mix up your anchor texts, just as you would with outbound links. This will help your site appear authentic and user-friendly to visitors and search engines.
Here are the main types you should rotate between for internal links:
Exact Match
This type of anchor text uses the target page’s primary keyword exactly as it appears.
For example, in the example below, the words “4xx error” link to a 4xx error guide.
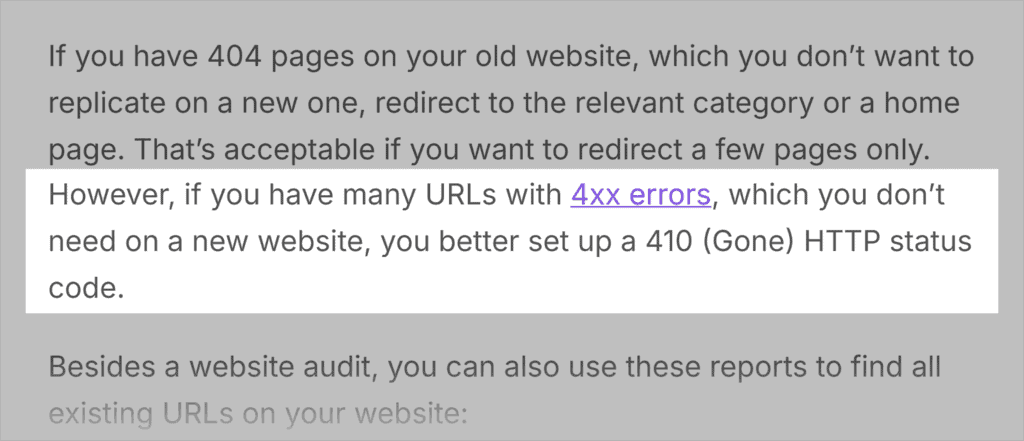
It’s tempting to default to this type of anchor text, but don’t overdo it. Switch up your anchor texts to provide more context to Google.
Partial Match
This is exactly what it sounds like — partial match anchor text includes the target keyword along with other words.
Here’s what this looks like in action:
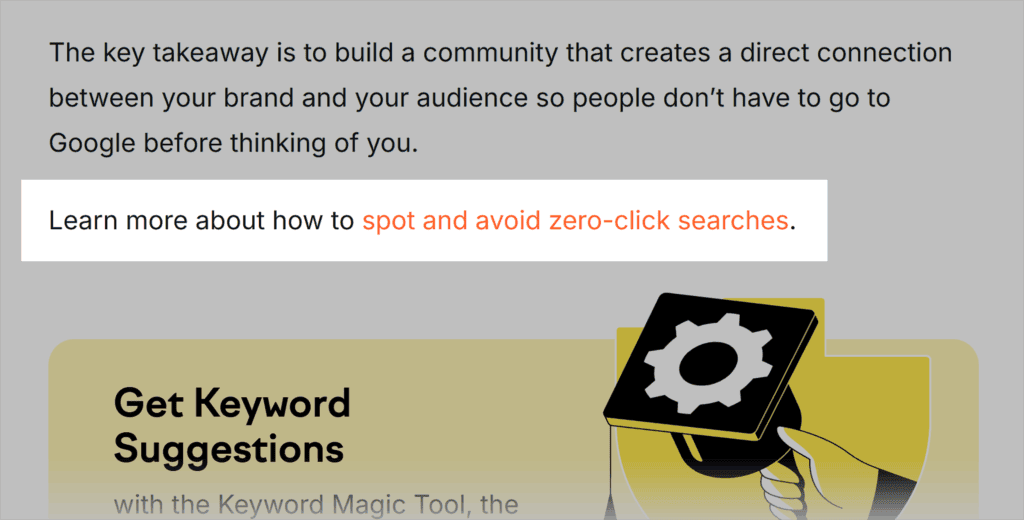
The words “spot and avoid zero-click searches” link to a guide on zero-click searches, making this partial match anchor text.
Branded
When you use your brand’s name as anchor text, it’s considered “branded.”
So, linking “Semrush” would be branded anchor text, as you can see in this example:
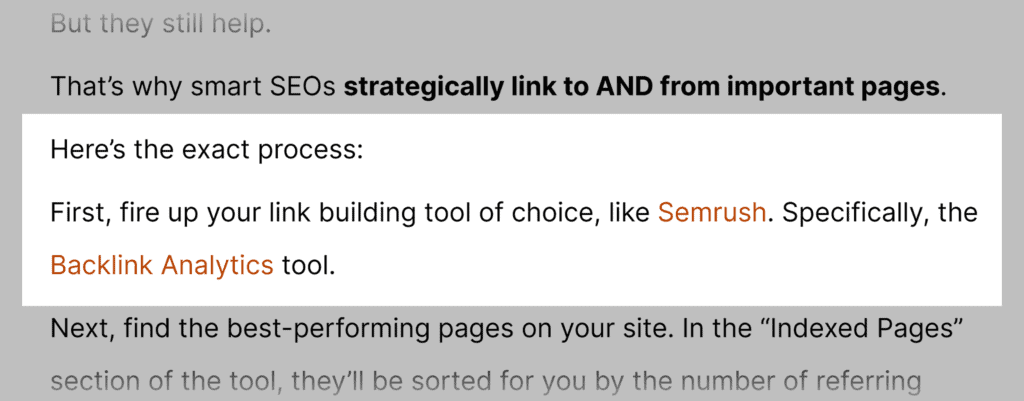
Compound
Similar to branded, compound anchor text is when you include your brand’s name along with other words.
For example, linking “Semrush review” would be considered compound anchor text since it includes the brand’s name plus “review.”
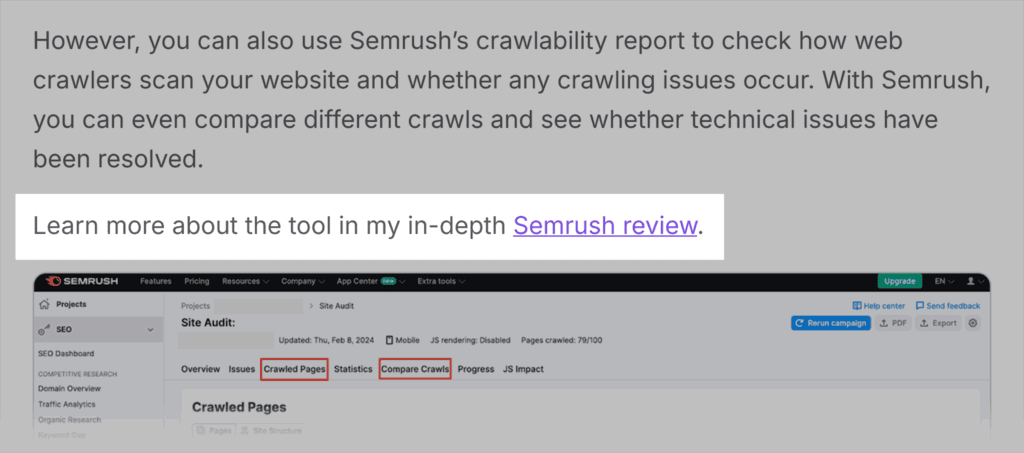
Related
Related anchor text describes what the reader will find without using exact keywords.
In this example, the words “structured data” link to a schema markup guide, making it related anchor text.
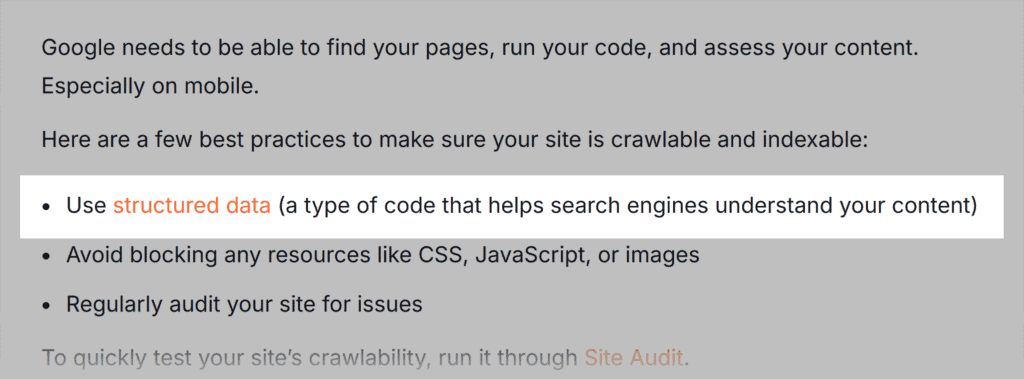
OK, we’ve covered the types of anchor texts to use for internal linking.
Now, let’s talk about what to avoid: generic or vague anchor text.
Examples include:
- Click here
- Learn more
- Read this
- Check it out
- This link
Also, avoid misleading and irrelevant anchors that don’t match the destination content. If you’re linking to a technical SEO guide, don’t use anchor text like “content marketing tips.”
2. Build Content Pillars
Content pillars, which are comprehensive and authoritative pieces covering core topics, should form the backbone of your content strategy.
Integrating internal links within these pillars is crucial for content organization and SEO.
To organize your pillar content with internal linking, link each pillar article to and from related cluster articles. This creates a network of relevant content, making it easier for users and search engines to find and understand the scope of your expertise.
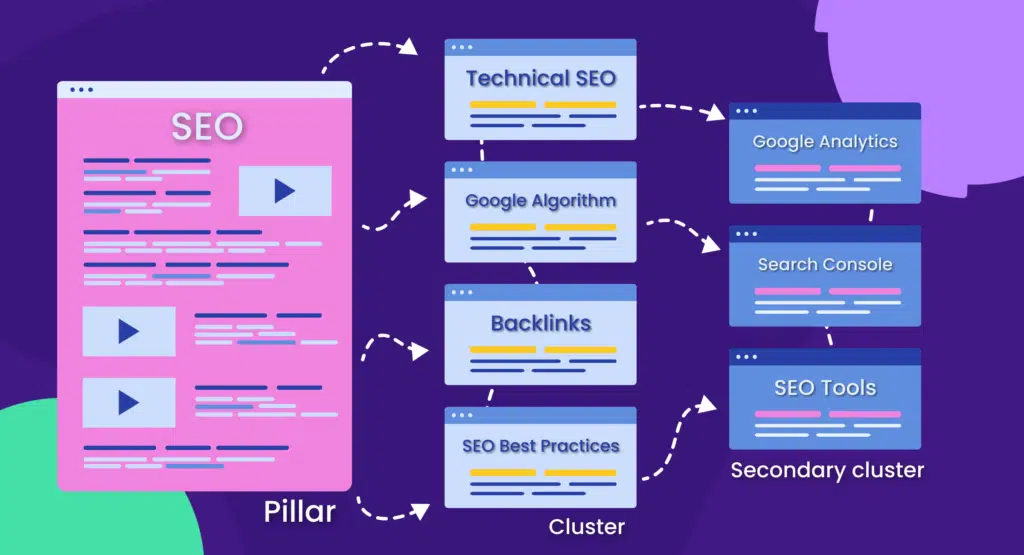
For example, if your pillar article is “The Complete Guide to Email Marketing,” you might link to supporting articles like:
- Email Segmentation Strategies That Boost Open Rates
- How to Write Subject Lines That Get Clicked
- Email Automation Workflows for Ecommerce
Likewise, the supporting articles should link back to your main pillar with relevant and descriptive anchor text.
This reinforces the pillar’s authority while creating a cohesive content network.
Place links where they naturally fit in the context of the text, so they guide readers to more in-depth content on related topics. This improves user experience and strengthens topical relevance.
Pro tip: Interlinked topic clusters can boost your chances of showing up in AI search engines and LLM responses. Cover relevant topics thoroughly and connect related pages with smart internal links to signal authority and depth.
3. Fix Keyword Cannibalization
Keyword cannibalization can occur when multiple pages on your site compete for the same keywords and intent and dilute each other’s search potential.
Internal linking can be a strategic tool to mitigate this issue.

How?
Use internal links to establish a hierarchy between pages. Link from less important pages to the most relevant or authoritative page for a specific keyword. This tells search engines which page should rank higher for those terms.
Say you have three pages targeting “email marketing automation” — a tool listicle, comprehensive guide, and case study. You might link from the blog post and case study to the guide using anchor text like “complete email automation strategy” or “definitive email marketing automation guide.”
Another option? If you have multiple pages covering the same topic and the same search intent, consider merging them when appropriate. This approach can consolidate the SEO value and provide clearer navigation for users.
So, how do you know if you have cannibalization issues? Many SEO tools can quickly scan your site and alert you to issues.
For example, Screaming Frog’s SEO Spider Tool analyzes page titles, meta descriptions, and headers to help you spot pages competing against each other so you can plan your internal links more effectively. (It’s also a recommended tool for programmatic SEO.)

Semrush’s Site Audit is another handy tool for identifying cannibalization and link issues.
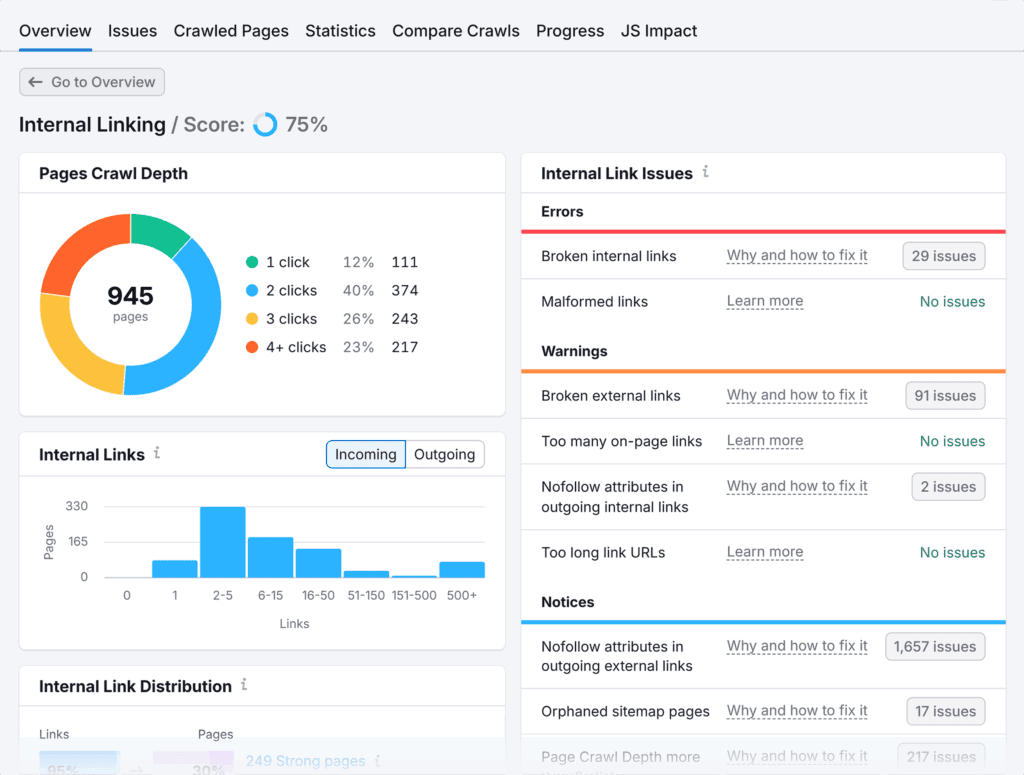
It helps you:
- Identify pages with too many or too few internal links
- Find broken internal links needing immediate attention
- Spot orphaned pages getting no internal link love
- Analyze anchor text distribution patterns
- Monitor internal linking between key pages
Regular monthly audits help catch and fix issues before they impact your SEO performance.
4. Improve the User Experience
Smart internal linking creates a seamless visitor journey that naturally guides users toward conversion.
Check Google Analytics to identify pages on your website with higher engagement rates and strategically link to them.

These pages usually feature compelling content and strong calls to action that encourage conversions.
You can boost your rankings and increase potential revenue by directing more traffic to these high-converting pages through internal links.
When integrating internal links, focus on adding value to the user experience rather than disrupting the reader experience.
Link to content that:
- Answers follow-up questions that your current page raises
- Provides deeper detail on topics you mention briefly
- Offers practical tools or resources related to your content
Avoid linking solely for keyword targeting or ranking manipulation. Links should be integrated naturally into your content so they feel like an integral part of the user’s journey through your website.
This ensures that your links guide users to related content that enriches their experience, rather than distracting or detracting from it.
Accordingly, if you ever perform an SEO migration for your website, minimize redirects and double-check that your internal and external links have remained intact.
Pro tip: Find valuable internal linking opportunities that improve the user experience by following this process:
- Use site search (site:yourdomain.com keyword) to uncover related content
- Maintain a content inventory grouped by topic clusters
- Identify high-authority pages that could boost newer content
- Review analytics to find high-converting pages worth featuring
- Study competitor sites for content relationship ideas
5. Speed Up Linked Pages
Fast-loading pages keep users engaged and bounce rates low, creating a better user experience for visitors. So, each time you link to an internal page, that linked page should load quickly.
Page load speed is also a direct ranking factor in search engine algorithms. Google has explicitly stated that it uses site speed in its ranking algorithms. Search engines view faster sites as more efficient and user-friendly, which leads to better rankings.
Here are some quick tips for improving page load speed:
- Optimize image sizes: Large images often slow down page loading times. Use compression tools like TinyPNG to reduce file sizes without sacrificing quality.
- Make your code as efficient as possible: Minimize CSS and JavaScript, and remove any unnecessary characters from your source code.
- Leverage browser caching: Caching stores elements of your pages in users’ browsers to decrease load time for repeat visitors.
- Consider a hosting switch: Evaluate your hosting solution and server response time, because these can significantly impact page loading speed.
You can use PageSpeed Insights to check the loading speed of your website and discover any technical issues that prevent it from loading fast.

6. Create Backlink Magnets
Strategic internal linking helps attract backlinks by making your best content more discoverable and demonstrating topical authority.
Backlinks are links from other websites to yours, and they’re one of the strongest ranking signals. The challenge is getting them naturally.

When other site owners can easily find and navigate your most valuable resources, they’re more likely to reference and link to them.
One way to do this is by linking heavily to your best content.
Identify your most comprehensive, data-rich, or unique pieces and link to them frequently from related articles. Create clear routes to your linkable assets like original research, comprehensive guides, or tool roundups.
While you can link to internal content in webpages, you can also use your website’s navigation strategically.
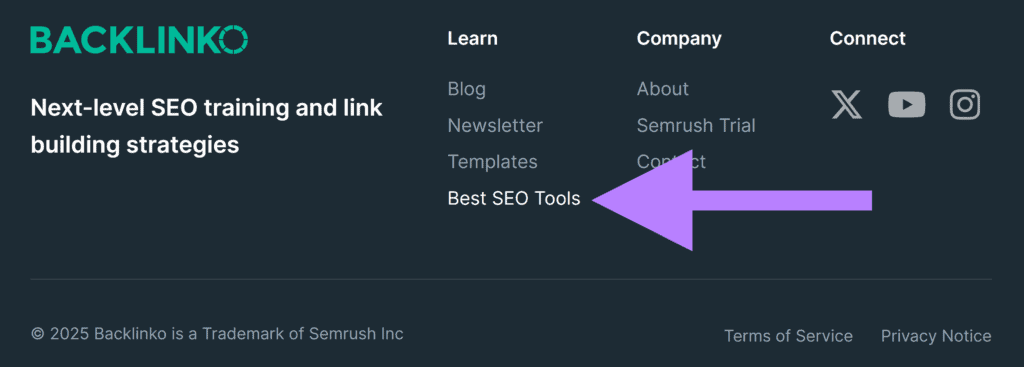
Pro tip: Keep important pages within three clicks from your homepage. Shallow link depth improves crawl efficiency and gets your key content indexed faster.
For example, Backlinko links to a high-impact blog post on the best free SEO tools in its footer.
Another smart idea? Use internal linking to promote your existing content. Regularly link to high-quality older posts from new articles to keep them visible and accessible.
When journalists or bloggers research topics in your niche, this helps them find your most valuable resources instead of just your latest posts.
You’ll also want to consistently link between articles on the same topic to demonstrate depth of coverage. If someone lands on any article about “content marketing,” your internal links should make it obvious you have comprehensive topical expertise.
These authority signals make external sites more confident in linking to your content.
7. Add Breadcrumb Navigation
Breadcrumbs are a navigational feature that helps users and search engines understand the layout and hierarchy of your website.
With breadcrumb navigation, you display a link trail showing the path to the current page within the site’s hierarchy.
They’re beneficial for sites with a complex structure or extensive content because they help users navigate and understand the website’s layout.
Additionally, they can reduce bounce rates and increase user engagement by offering visitors an easy way to navigate deeper into your website. Low bounce rates and high user engagement signal to search engines that your site is user-friendly and valuable.
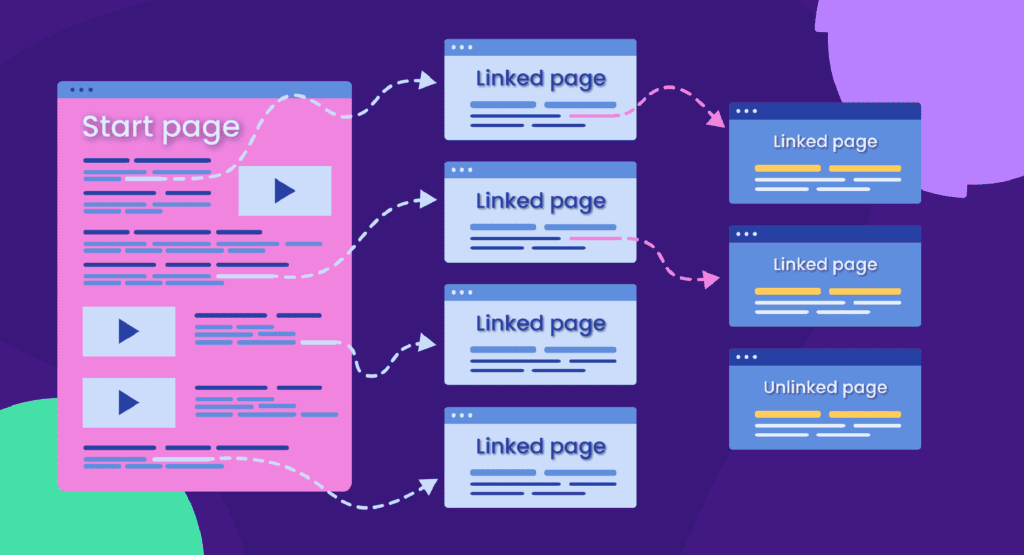
For simpler websites with a linear or minimalistic design, breadcrumbs might be unnecessary and can clutter the interface.
There are three main types of breadcrumbs:
- Hierarchy-based breadcrumbs: Shows the position of a page within the site’s structure. Implement these when your site has a multi-level layout so users can easily navigate back to higher-level categories.
- Path-based breadcrumbs: Tracks the user’s journey through the site. They are less common and useful for sites where users are likely to follow varied paths to reach a page.
- Attribute-based breadcrumbs: Often used in ecommerce sites. They display attributes like brand, category, or size.
Pro tip: Not sure if links should open in a new tab? Think about your visitor’s journey — if they’d benefit from keeping their current page open, a new tab makes sense. Otherwise, stick with same-tab navigation to maintain their natural flow through your site.
Make Your Internal Linking Strategy Work Harder
Don’t sleep on internal links. Creating and maintaining a strong link strategy makes it easier for users and search engines to find your content.
First step? Get a clear picture of your current linking structure. Fire up Semrush’s Site Audit tool and prepare for some surprises.
You may find orphaned pages, broken links from 2022, and the dreaded generic anchor text.
Next, download our link audit checklist if you haven’t already. You’ll get actionable steps and tool recommendations to fix any issues.
Finally, read our crawlability and indexability guide to help search engines discover your site and rank your pages faster.